Study Dissects the Complete Plastid Genome and Phylogeny of Polystachya (Orchidaceae) Species from Kenya
2022-07-04
As a large pantropical orchid genus, Polystachya Hook.,comprises approximately 240 species, most of which are distributed in Africa. Up to now, studies on the complete chloroplast genomes and the phylogenetic position of the genus in the Orchidaceae are limited.
Researchers from Wuhan Botanical Garden sequenced the complete chloroplast genomes of six Kenya Polystachya species, conducted comparative genomic analysis, and reconstructed the phylogenetic tree to explore the phylogenetic position of Polystachya in Orchidaceae.
The results indicated that the plastid genomes of the six Polystachya species had a typical quadripartite structure with lengths ranging from 145,484-149,274 bp. A total of 106-109 single-copy genes were encoded in these plastomes, and all ndh genes were lost or pseudogenized in their plastid genomes (Figures 1 and 2).
Comparative genomic analysis revealed varying degrees of expansion in the inverted repeat (IR) region of the six Polystachya plastomes, and this expansion was associated with denormalization of the ndh genes; an inversion of approximately 1 kb was found only in the IR border region in P. modesta. In addition, they screened seven highly variable regions that could be used to develop DNA genetic markers and identified 13 genes with significant positive selection.
Phylogenetic analysis based on the current plastid genomic data revealed that Polystachya was monophyletic, identified the phylogenetic position of Polystachya in the tribe Vandeae, and largely established the phylogenetic relationships of most taxonomic units in the tribe and above tribe of Orchidaceae (Figures 3).
This study provides important data for the plastid genomic study of the genus Polystachya, which is significant for future phylogenetic studies and species evolution regarding this genus and the subtribe Polystachyinae.
The research results were published in the international botanical journal BMC Plant Biology under the title “Comparative and phylogenetic analyses of six KenyaPolystachya(Orchidaceae) species based on the complete chloroplast genome sequences”.
This work was jointly carried out by the Wuhan Botanical Garden of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and the National Museum of Kenya, and was supported by the International Partnership Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences, the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Sino-Africa Joint Research Center, CAS.
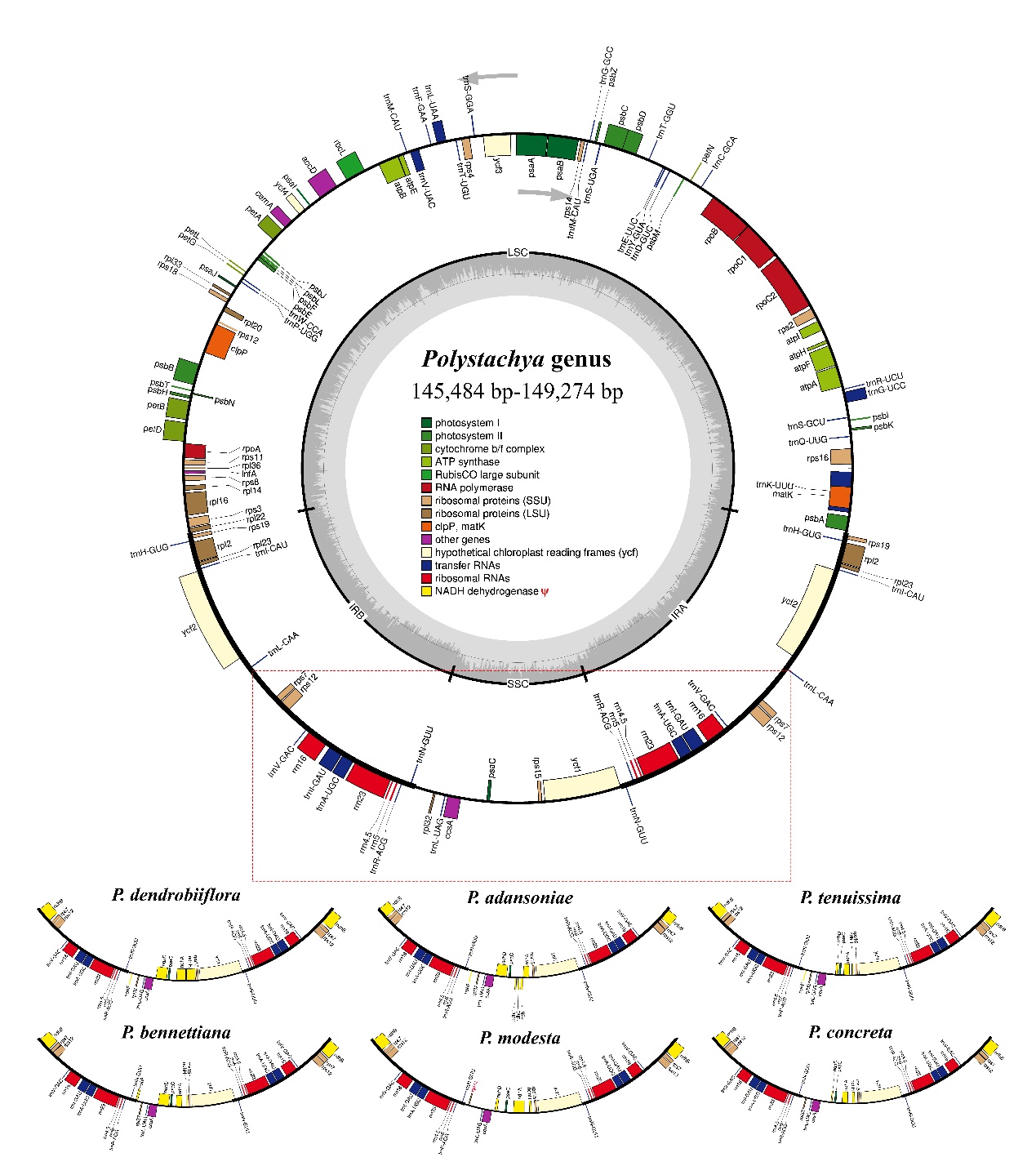
Figure 1. Chloroplast genome map of six Polystachya species (Image by WBG)
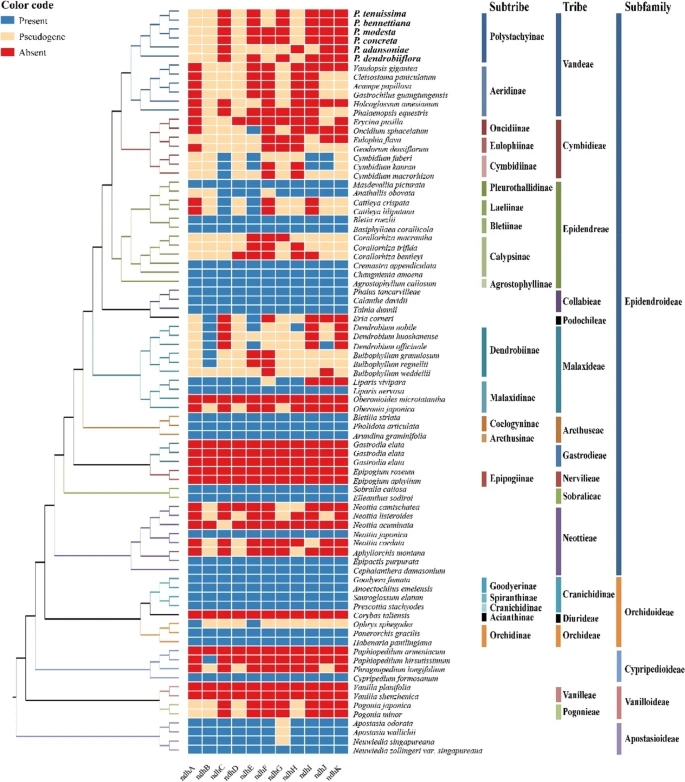
Figure 2. Distribution patterns of ndh gene loss in Orchidaceae (Image by WBG)
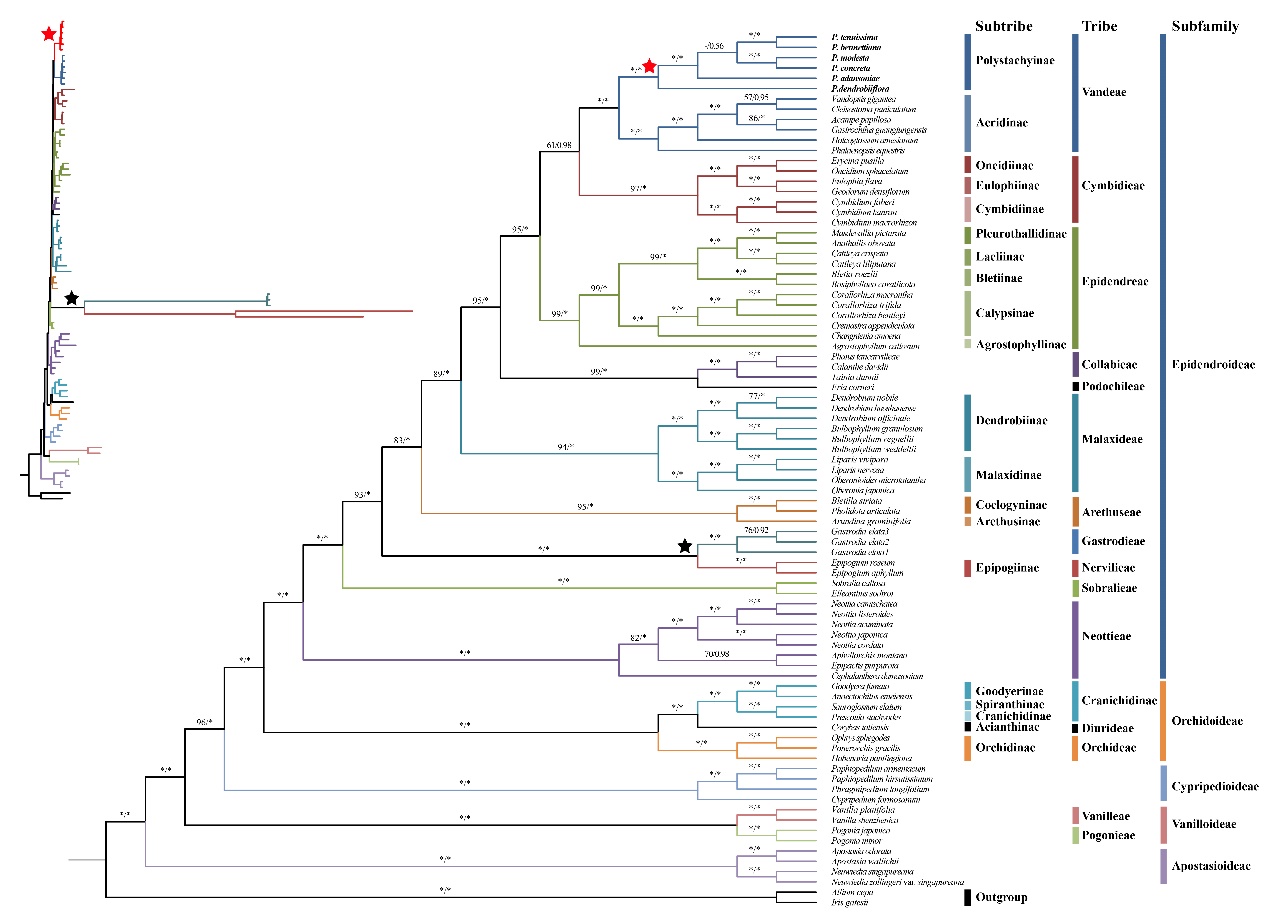
Figure 3. Phylogenetic tree constructed using Maximum Likelihood and Bayesian Inference methods, based on the 79 concatenate protein-coding sequences of whole cp genomes from 85 taxa (Image by WBG)