How is Flesh Surrounding the Stone Colored in Peach?
2023-04-04
Red coloration around the stone (Cs) is a unique phenomenon in peach. It happens due to the accumulation of anthocyanin and is associated with fruit ripening, which is not conducive to the development of canned peaches. However, it is not clear how the anthocyanin accumulates surrounding the stone.
Supervised by Prof. HAN Yuepeng of Wuhan Botanical Garden, research assistant ZHAO Lei cloned the PpHY5 gene, an important gene participated in the regulation of the Cs trait, and its expression was consistent with anthocyanin accumulation surrounding the stone.
A series of studies showed that PpHY5 promoted the activation of anthocyanin regulator gene PpMYB10.1 in the present of a cofactor PpBBX10. An E3 ubiquitin ligase gene PpCOP1 was moderately expressed in the flesh around the stone at the later stages of fruit development and could interact with PpHY5. Although HY5 (a pivotal regulator of anthocyanin accumulation in a light dependent manner) is usually degraded by constitutive photomorphogenesis protein 1 (COP1) through ubiquitination, the PpHY5 gene was activated in the red-colored flesh tissue around the stone at the ripening stages.
This study firstly reveals that the PpHY5 gene is involved in the anthocyanin accumulation surrounding the stone, which is helpful for comprehensive understanding of the complex mechanisms underlying anthocyanin accumulation in peach fruit.
This work was published in The Plant Journal entitled “PpHY5is involved in anthocyanin coloration in the peach flesh surrounding the stone”. It was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China, National Natural Science Foundation of China, the China Agriculture Research System and Hubei Hongshan Laboratory. (First published: 15 March 2023)
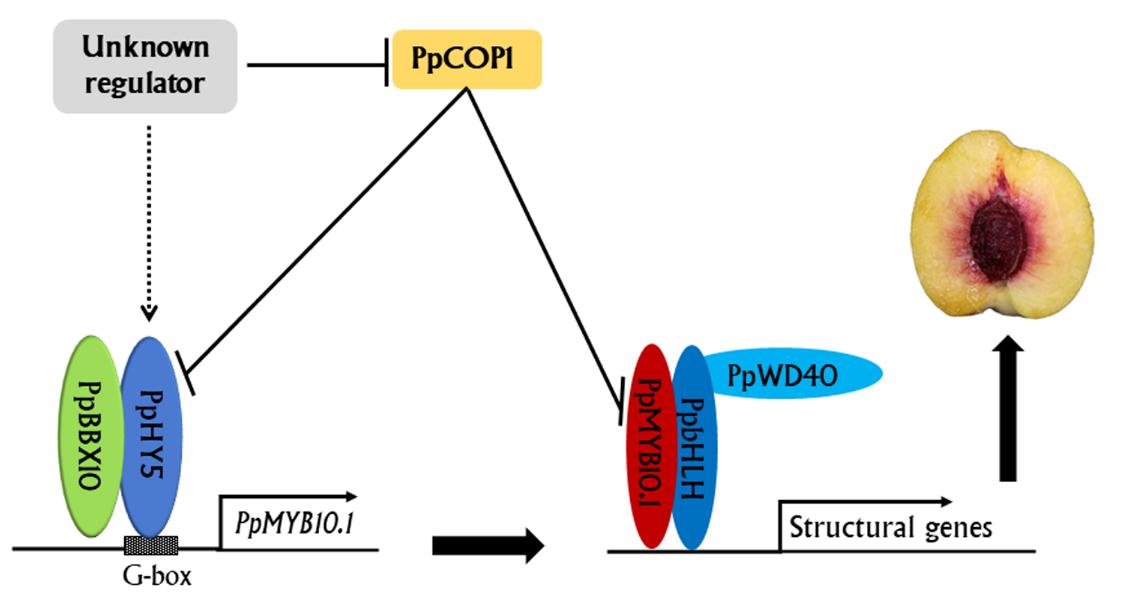
The regulatory network model for PpHY5 involved in anthocyanin coloration in the peach flesh surrounding the stone (Image by ZHAO Lei)