Lotus is an important ornamental plant and a commercial crop with great cultural and religious significance. It is also one of the top ten famous Chinese traditional flowers. Its flower is big and beautiful, often used as an ornamental plant in water fields in summer.
Petal color is one of the major characteristics that determine the ornamental value of lotus. In order to assess the contribution of different flavonoids to this character, PhD student Jiao Deng at the supervision of Professor Pingfang Yang from Key Laboratory of Plant Germplasm Enhancement and Speciality Agriculture, Wuhan Botanical Garden analyzed flavones and flavonols through high performance liquid chromatography coupled with photodiode array detection tandem electrospray ionisation triple quad mass spectrometry in 108 lotus cultivars with red, pink, yellow, white and red/white pied petal colors.
Results showed that five anthocyanins and fourteen flavones and flavonols were detected and quantified. In general, the yellow, white and pied species hardly contained any anthocyanins; red cultivars contained more than pink cultivars. Among the five anthocyanins, malvidin 3-O-glucoside was the most abundant one in all the cultivars that contain anthocyanin, which showed that the red color of lotus petal is positively correlated with anthocyanins conten. Flavons and flavonols, taken as accessory pigments, seemed to contribute a little to the yellow color. In this study, principal component analysis (PCA) was conducted. Based on their percentage of contribution, two principal components, PC1 and PC2, were determined. PC1 was largely decided by the total anthocyanins content; PC2 was related to the total content of flavones and flavonols and content of two anthocyanins. By using PCA, most of the cultivars could be sorted into 3 groups (A, B and C). Group A exclusively contained mostly red and several pink cultivars due to high content of total anthocyanins. Group B contained most of the yellow cultivars, small part of pink and pied color cultivars and two white cultivars due to high content of flavones and flavonols. Group C contained most of the white cultivars due to low content of total anthocyanins, flavones and flavonols. From the results of PCA, it can be concluded that the content of anthocyanins is highly and positively correlated with red color, while the content of flavones and flavones is positively related with yellow color. These data might be helpful in lotus breeding for different colors.
Results were published in Food Chemistry entitled "Systematic qualitative and quantitative assessment of anthocyanins, flavones and flavonols in the petals of 108 lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) cultivars”.
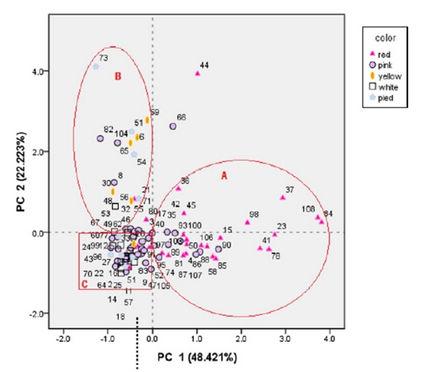
Positions of PC scores of 108 lotus cultivars
