Kava is a plant native to the South Pacific. The root is used for medicine. It can be used to calm anxiety, stress, and restlessness, and treat sleep problems (insomnia). It is also used for attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), epilepsy, psychosis, depression, migraines and other headaches, chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), common cold and other respiratory tract infections, tuberculosis, muscle pain, and cancer prevention. Kavalactones, the main psychoactive components of kava, exert advantageous physiological functions on humans such as diuretic, soporific, antiepileptic, spasmolytic, analgesic, local anaesthetic, bacteriocidal and antimycotic functions.
Kava’s beneficial effects have been recognized in many countries, such as the Britain and the United States. The South Pacific islanders have consumed kavabeverage for thousands of years. However, no studies were reported about extraction efficiency of kavalactones using different organic solvents in kava material and kava beverage.
Prof. WANG Jun from Wuhan Botanical Garden studied chemotypes and contents of kavalactones from rhizomes and roots of two kava varieties in five different solvents and extraction efficiency of different solvents for kavalactones from kava materials.
In this study, they determined contents of kavalactones in and chemotype of kava beverages prepared from roots and rhizomes of Isa and Mahakea varieties and extraction efficiency of five different solvents including hexane, acetone, methanol, ethanol and ethylacetate. The six major kavalactones were detected in all kava beverages with these five solvents. Different solvents had different extraction efficiencies for kavalactones from the lyophilized kavapreparations. The contents of kavalactones in the extracts with acetone, ethanol, and methanol did not differ significantly. Ethanol had the highest extraction efficiency for the six major kavalactones whereas hexane gave the lowest extractionefficiency.
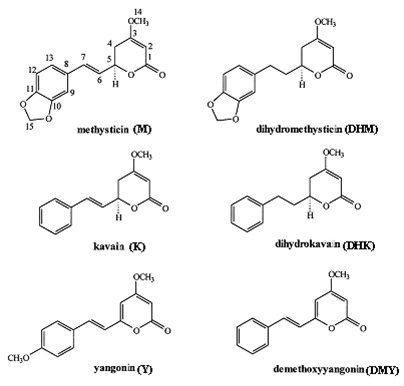
Molecular structuresof the six major kavalactones(Image by Prof. WANG Jun)
