Name:WANG Jun
Tell:
Email:wangjun@wbgcas.cn
Organization: Wuhan Botanical Garden
Distribution, Seasonal Variations and Ecological Risk Assessment of PAHs Evaluated in the East Lake
2016-02-25
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are neutral, nonpolar organic contaminants that built from two or more benzene rings, which originate primarily from both natural and anthropogenic sources and the latter are by far the major contributors. PAHs are ubiquitous pollutants in the environment that can be introduced into aquatic environments. As rivers, lakes and reservoirs are frequently used for potable water sources, their contamination is particularly undesirable. Therefore, investigations of PAHs in aquatic environments are imperative, which are important to understand the status of contamination and evaluate the potential risk to the ecosystem.
YUN Xiaoyan, under the supervision of Professor WANG Jun, from Wuhan Botanical Garden evaluated the concentrations, distributions, seasonal variations, sources and risk assessment of PAHs in surface water and sediments from the East Lake.
The residues of 16 PAHs detected in surface water and surface sediment collected from the East Lake, China indicated a wide occurrence of PAHs in this study area. The PAHs total concentrations in water and sediment ranged from 10.2 to 525.1 ng L-1 and 10.9 to 2478.1 ng g-1 dry weight (dw), respectively. The concentrations of ∑PAHs in sediment samples in summer were twice as much as those in winter,but the seasonal variations were not much different in water samples.
Diagnostic ratios of indictor PAHs reflected pyrolytic PAH from incomplete combustion of fossil fuels predominated in sediment and mixture sources of pyrolytic and petrogenic in water from the East Lake. The potential ecological risk assessment based on risk quotient (RQ) indicated relatively moderate ecological risks of PAHs in the East Lake.
Results were published in CLEAN-Soil, Air, Water, entitled “Distribution, seasonal variations and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the East Lake, China”.
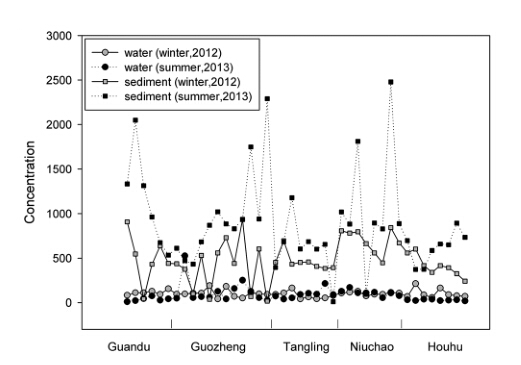
Distribution pattern of ∑PAHs in water and sediment from the East Lake (Image by YUN Xiaoyan )