Name:Tao Shi
Tell:
Email:shitao323@wbgcas.cn
Organization:Wuhan Botanical Garden
Whole Genome Re-sequencing Reveals Evolutionary Patterns of Lotus
2017-11-14
Sacred lotus has been widely cultivated in China since about 2205 B.C due to its ornamental, edible, pharmacological and religious importance. Understanding the genomic diversity and relationship of lotus is important to the breeding, in-situ and ex-situ conservation of key germplasms.
In order to explore genomic variation and evolution among different germplasms, HUANG Longyu, supervised by Prof. YANG Pingfang and Assistant Prof. SHI Tao from Wuhan Botanical Garden, resequenced and analyzed the genomes of 19 lotus germplasms, representing rhizome lotus, seed lotus, flower lotus, temperate lotus, tropical lotus and the outgroup American lotus.
Chinese wild lotus and Thai lotus exhibited greater differentiation with a higher genomic diversity compared to cultivated lotus. Rhizome lotus had the lowest genomic diversity and a closer relationship to wild lotus, whereas the genomes of seed lotus and flower lotus were admixed.
Genes in energy metabolism process and plant immunity evolved rapidly in lotus, reflecting local adaptation. Candidate genes in genomic regions with significant differentiation associated with temperate and tropical lotus divergence always exhibited highly divergent expression pattern.
This study provied a comprehensive and credible interpretation of important patterns of genetic diversity and relationships, gene evolution, and genomic signature from ecotypic differentiation of sacred lotus.
Results entitled “Whole genome re-sequencing reveals evolutionary patterns of sacred lotus (Nelumbo nucifera)” were published in Journal of Integrative Plant Biology. It was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China .
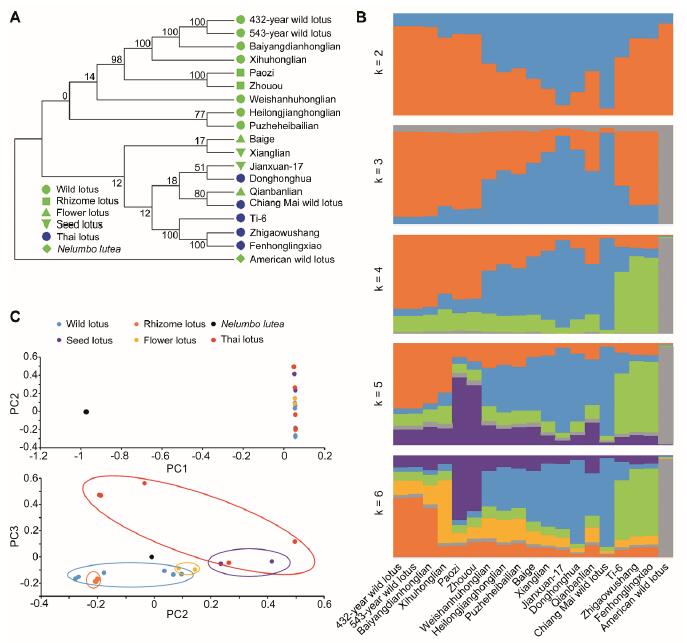
Phylogenetic, population stratification and principal component analyses (PCA) of 19 lotus germplasms (Image by HUANG Longyu)