Name:LI Wei
Tell:
Email:liwei@wbgcas.cn
Organization:Wuhan Botanical Garden
Thiol Groups Determine How Silver Nanoparticles and Proteins Interact?
2019-06-14
Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) are widely used in various fields of human production and life due to their excellent antibacterial properties. However, AgNPs are also toxic to various organisms when they are discharged into the environment.
When discharged into the environment, AgNPs could be internalized by organisms and then surrounded by proteins. Once the interaction between the AgNPs and proteins occurs in the cells, the AgNPs can alter protein conformation inducing unexpected biological reactions and lead to cytotoxicity. However, the interactions between AgNPs and proteins, especially the role of thiol groups in the interaction need further research.
Most proteins in the organism contain at least one thiol group, which may function as the active site or stabilize the structure of the protein in these proteins. Under the guidance of Prof. LI Wei and Prof. Brigitte Gontero, JIANG Hongsheng, an associate Professor of the Laboratory of Aquatic Plant Biology of Wuhan Botanical Garden, conducted the experiments to study the interaction between AgNPs and proteins.
The enzyme glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), which plays a key role in glycolysis and Calvin cycle, and malic acid dehydrogenase (MDH), a key enzyme in the Krebs cycle and the C4 metabolic pathway, were selected to model these interactions.
The results showed that the thiol groups in both GAPDH and MDH bound to silver, resulted in a significant reduction in the content of free thiol groups, thereby reducing the activity of these two enzymes. Based on the comparison of half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values of enzyme activities, it was found that AgNPs interacted with thiol groups in proteins by releasing Ag ions.
If the enzyme active site contains a thiol group, such as GAPDH, the enzyme rapidly loses its activity after the Ag binding on the thiol group. In the contrast, if the enzyme active site without any thiol group, such as MDH, the secondary structure of the protein changes and results in the loss of enzyme activity after the Ag binding on the thiol groups at other sites. In summary, the location of the thiol group in the protein and its function determine the way of the interactions between proteins and AgNPs.
This study comprehensively elucidates the roles of thiol groups in the interactions between proteins and AgNPs, which could fill the gap to decipher better the toxic mechanisms of AgNPs.
The research was supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the results were published in the internationally journal Small entitled "Interaction between Silver Nanoparticles and Two Dehydrogenases: Role of Thiol Groups".
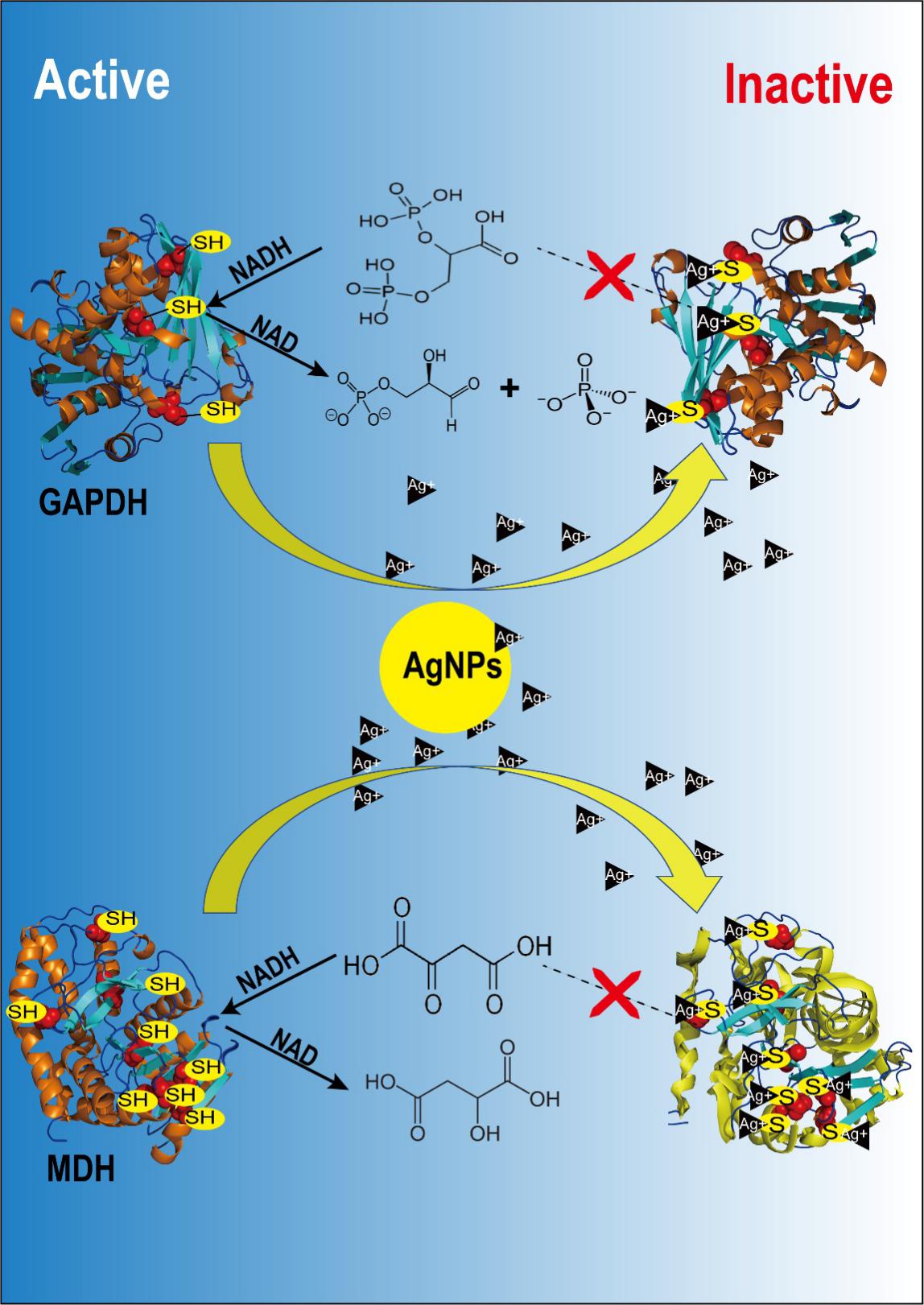
Schematic diagram of the interaction between silver nanoparticles and GAPDH and MDH (Image by JIANG Hongsheng)