Name:LIU Feng
Tell:
Email:liufeng@wbgcas.cn
Organization: Wuhan Botanical Garden
Researchers Unveil Effects of Litter Chemistry on Lignin Degradation
2019-07-30
Lignin is an important organic component of plant litter, accounting for approximately 30% of litter carbon input annually. Due to its aromatic structure and recalcitrant properties, lignin has long been considered as a controlling factor for the buildup of the soil organic carbon pool. In addition, lignin chemistry are assumed to largely affect litter decay rates. However, lignin degradation and its controlling factors during litter decomposition are not fully understood.
Under the supervise of Professor LIU Feng, HE Mei , PhD from Wuhan Botanical Garden, explored the patterns of lignin degradation and its associated controlling factors during litter decomposition through a 180-day lab incubation experiment with leaves of two tree species (Fagus lucida and Schima parviflora) from a mid-subtropical forest in China.
The mass loss of bulk litter and lignin (including V-, S- and C-type phenols) and the dynamics of litter microbial community composition, carbon (C), nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) were determined during the incubation.
Results showed that lignin degradation appeared to be a two-phase process over the incubation period: a fast decomposition phase followed by a relatively slow decomposition phase.
The acid to aldehyde ratios of V-type phenols [(Ac/Al)V] and S-type phenols [(Ac/Al)S] of both litters increased with incubation. Lignin degradation was significantly affected by the litter types but not by the soil microbial communities. The mass loss of lignin in the early stage was significantly correlated with lignin, N and P contents, and the C/N, C/P and N/P ratios. These results improve the conceptual understanding of lignin degradation and its controlling factors.
The present study was supported by the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China. Related research results entitled “Predominant effects of litter chemistry on lignin degradation in the early stage of leaf litter decomposition” were published on Plant and Soil.
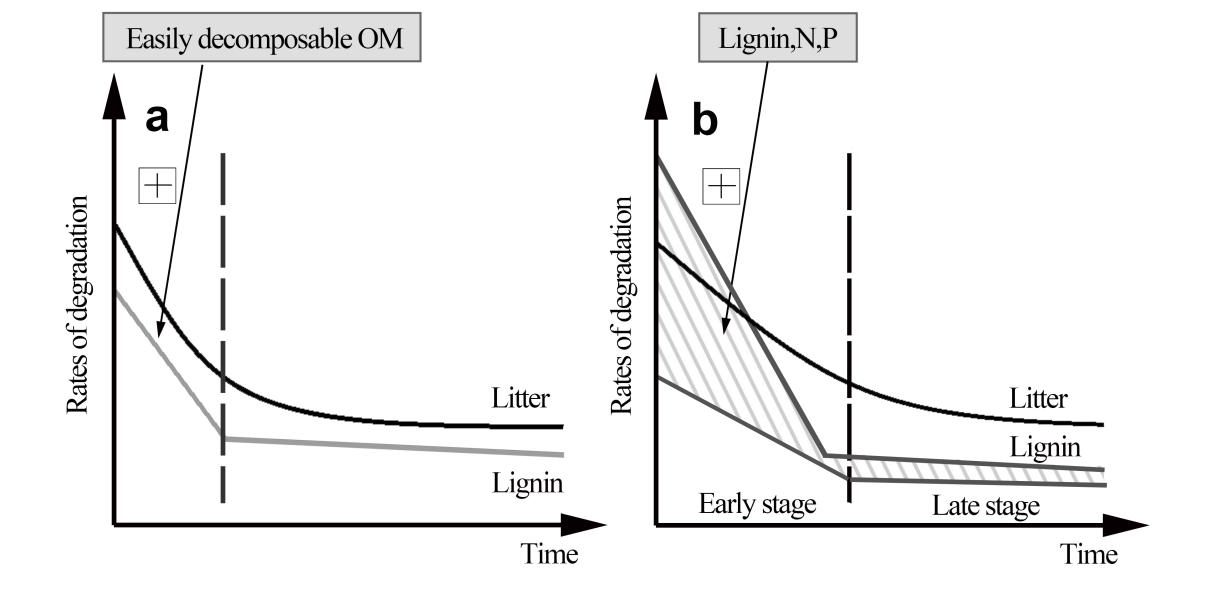
Conceptual model of lignin degradation and major controlling factors during litter decomposition (Image by WBG)