Name:Lin Ma
Tell:
Email:malin@wbgcas.cn
Organization:Wuhan Botanical Garden
The Mn(III)-pyrophosphate Complexes Enhance Arsenite Simultaneous Sorption and Oxidation by NFMO
2020-03-05
Arsenite [As(III)] is more toxic and difficult to be removed from aqueous systems compared to arsenate [As(V)], and thus poses a significant health risk to humans and the environment. Compared to synthetic adsorbents, the low cost and abundance of natural ferruginous manganese ore (NFMO) makes it a potentially attractive adsorbent for application in large-scale treatments.
Researchers from Wuhan Botanical Garden investigated As(III) oxidation and adsorption by three NFMOs with different Mn/Fe ratios.
The study demonstrated that the NFMO with a high Mn:Fe ratio had a stronger oxidation capacity for As(III), while As(III) adsorption efficiency of NFMOs increased with increasing Fe content. As(III) oxidation was strongly pH dependent, increasing as pH increased from 6 to 7.9. Moreover, the As(III) oxidation rate of NFMO increased by 68% with the addition of pyrophosphate (PP), and increasing PP concentrations led to higher oxidation rates.
More importantly, this study revealed the mechanisms of As(III) oxidation and adsorption by natural Fe-Mn. PP formed complexes with Mn(III), thus accelerating the conversion of Mn(IV) to Mn(III). Then the dissolution of these complexes led to a generation of additional oxidation adsorption sites, favouring As(III) oxidation. As(III) removal by NFMO was attributed to the joint effect of sorption and oxidation processes, where Manganese oxide was responsible for As(III) oxidation, while Fe oxide played a primary role in the arsenic sorption.
These findings highlight that addition of a liquid chelating agent, specifically PP, is a facile and effective method for enhancing As(III) oxidation performance of NFMO, making this a promising adsorbent system for practical wastewater treatment.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China. Dr. MA Lin (research assistant of Wuhan Botanical Garden) and CAI Dongmei are co-first authors of the paper (master of Huazhong Agricultural University). Professor TU Shuxin is the corresponding author (Huazhong Agricultural University). The relevant results have been published on Chemical Engineering Journal under the title “Arsenite simultaneous sorption and oxidation by natural ferruginous manganese ores with various ratios of Mn/Fe”.
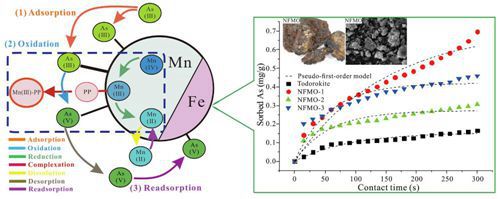
Mechanisms of As(III) oxidation and adsorption by natural Fe-Mn ore under pyrophosphate intervention (Image by MA Lin)