Name:HU Guangwan
Tell:
Email:guangwanhu@wbgcas.cn
Organization:Wuhan Botanical Garden
SAJOREC and NMK Researchers Cooperate to Investigate Medicinal Plants in Kenya
2020-04-10
A paper about the investigation on traditional medicinal plants of Mutomo Hill Plant Sanctuary and its environs in Kenya was published in the latest issue of the international journal, Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicines, titled “An Ethnobotanical Survey of a Dryland Botanical Garden and Its Environs in Kenya: The Mutomo Hill Plant Sanctuary” as an achievement of the cooperation of Kenyan and Chinese scientists.
There are 6,293 indigenous vascular plant species distributed in Kenya. Out of them, over 5,000 plant species reportedly occur in drylands. An estimated 1,200 plant species are reported to have medicinal value. The dryland areas of Kenya play an important role in sustaining the livelihoods of the local communities through the provision of important resources such as medicinal plants. Mutomo Hill Plant Sanctuary is a botanical garden under the Botanical Garden Conservation International.
Researchers from Sino-Africa Joint Research Center (SAJOREC), CAS and National Museums of Kenya (NMK) surveyed medicinal plants of Mutomo Hill Plant Sanctuary and its environs between July 2018 and February 2019. The collecting activities were guided by local herbalists, most of whom were older than 60 years.
In total, 69 medicinal plants used by the local communities were recorded. 24 plant species were found to be frequently used by the local communities. Among them, ethnobotanical applications of Moringa borziana are likely to be reported in Kenya for the first time. Among the vascular plant families, there were the most common plant species reported in Fabaceae family.
The local communities were found to obtain the medicinal plants from the farmlands, abandoned cultivations, bushlands and surrounding hills. Some plant species, such as Strychnos henningsii and Vepris simplicifolia which were found to be mostly obtained from the hills, were reported by the herbalists to be decreasing in the wild. Cassia abbreviata, Terminalia brownii, and Vepris simplicifolia were found to be sold at the Mutomo market.
There is a need for more ethnobotanical studies in Kenya at local levels, especially where floristic studies may not be prioritized due to lack of intact forests. There are likely many medicinal plants that were not documented during the study, hence there is a need for future surveys in both wet and dry seasons. The authors recommend Mutomo Hill Plant Sanctuary for the conservation of medicinal plants in the study area and Kitui county in general.
Map of Kenya showing the location of Mutomo division and Mutomo hill plant sanctuary (Image by SAJOREC and NMK)
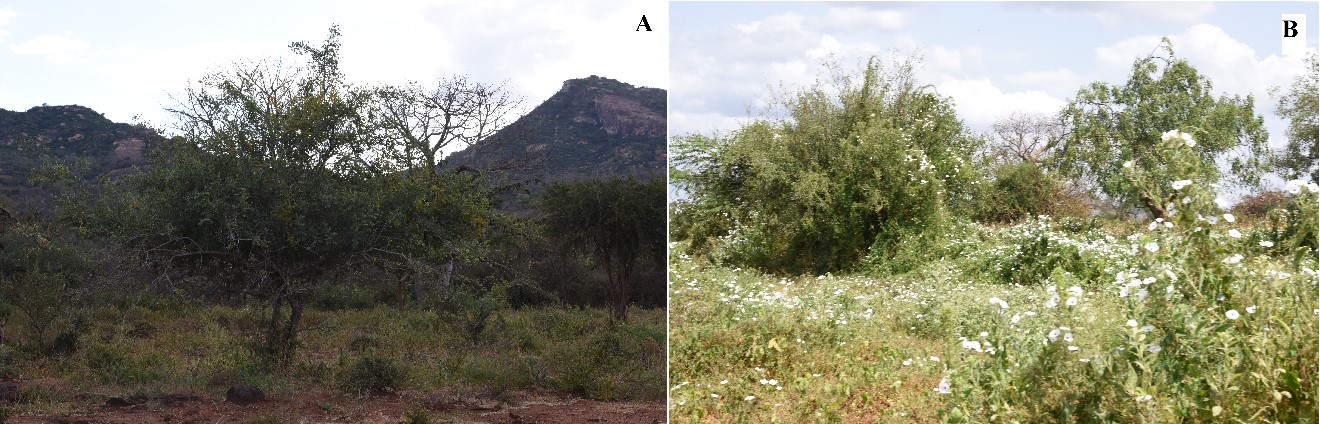

Some habitats where medicinal plants are collected in Mutomo hill plant sanctuary and its environs. A. Bushland and surrounding hills, B. Abandoned farmland (Image by SAJOREC and NMK)
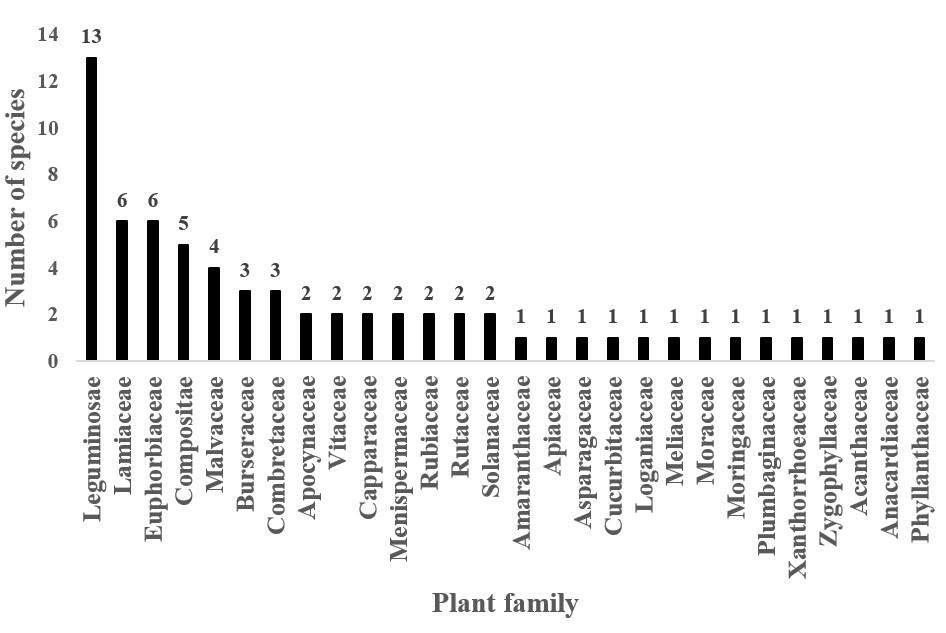
Distribution of the plant species in different families (Image by SAJOREC and NMK)
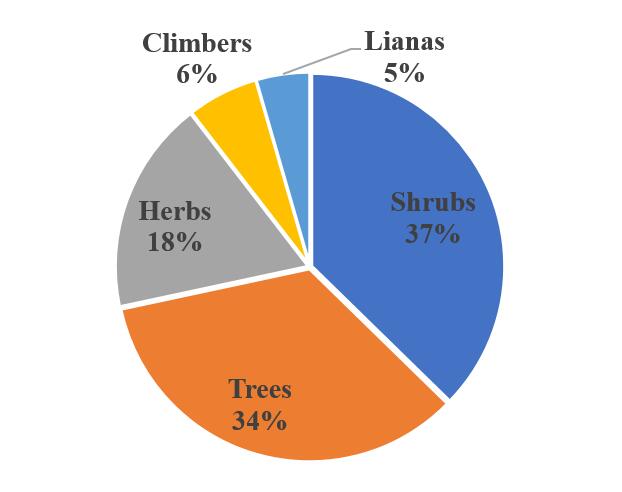
Distribution of plant growth habits (Image by SAJOREC and NMK)
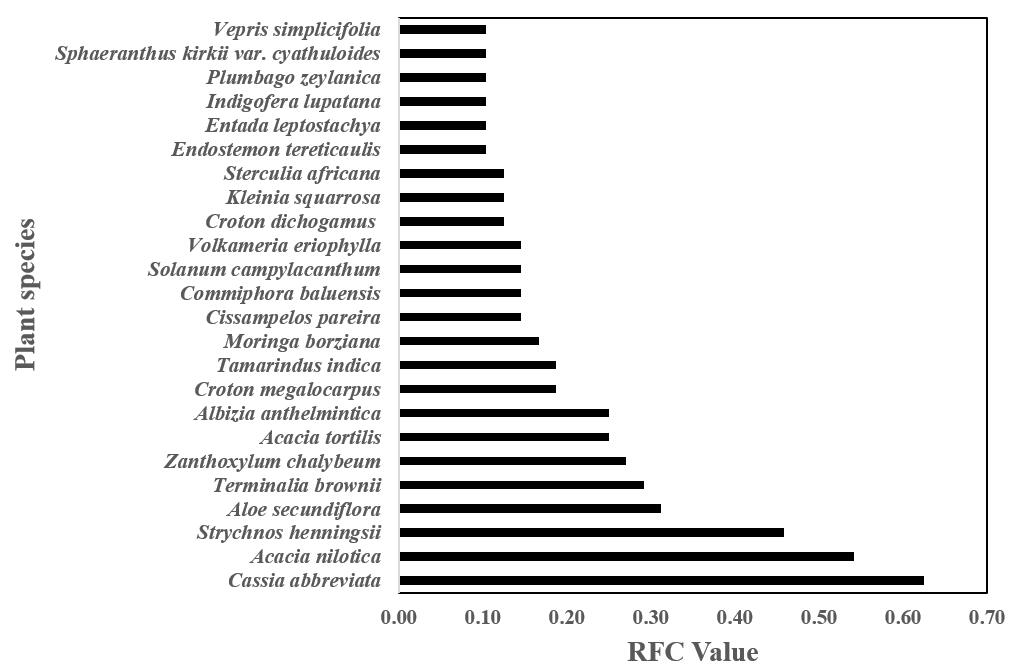
Frequently used plant species (Image by SAJOREC and NMK)
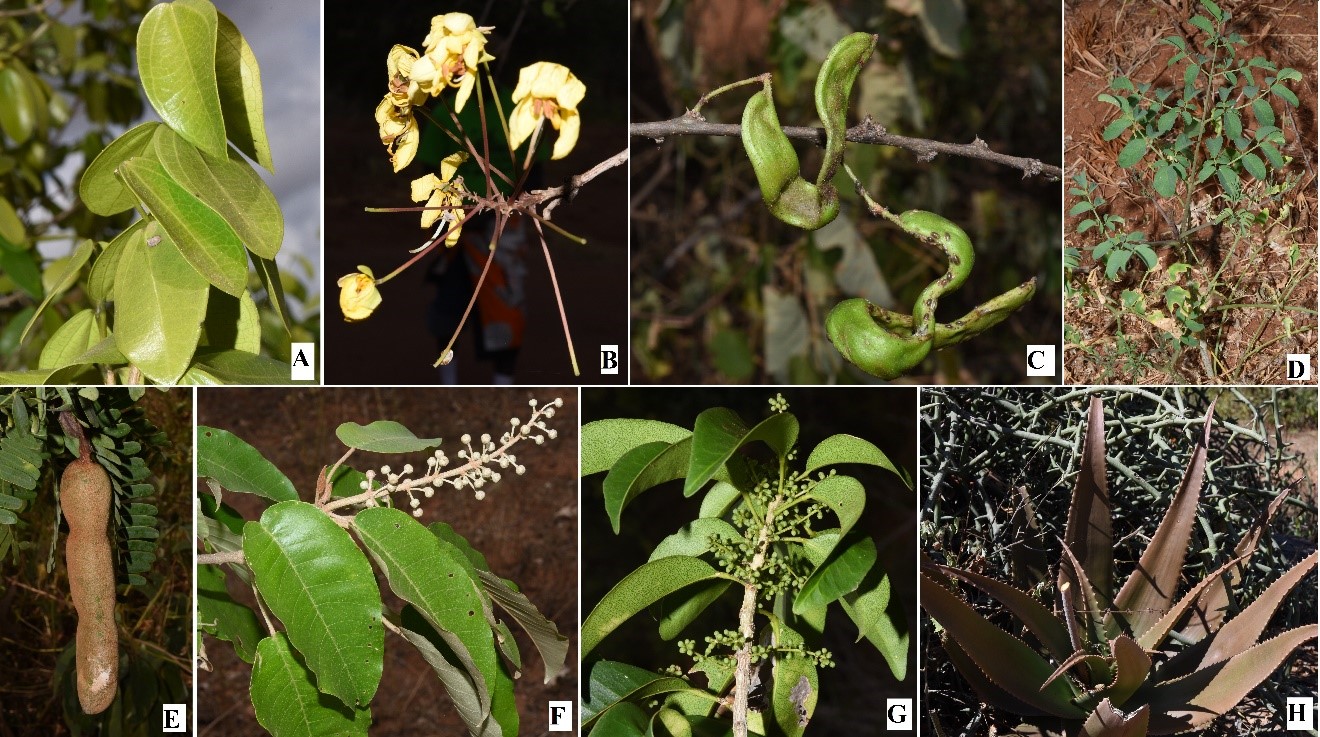

Some frequently used medicinal plants of Mutomo hill sanctuary and its environs. A. Strychnos henningsii, B. Cassia abbreviata, C. Acacia tortilis, D. Moringa borziana, E. Tamarindus indica, F. Croton megalocarpus, G. Vepris simplicifolia, H. Aloe secundiflora (Image by SAJOREC and NMK)
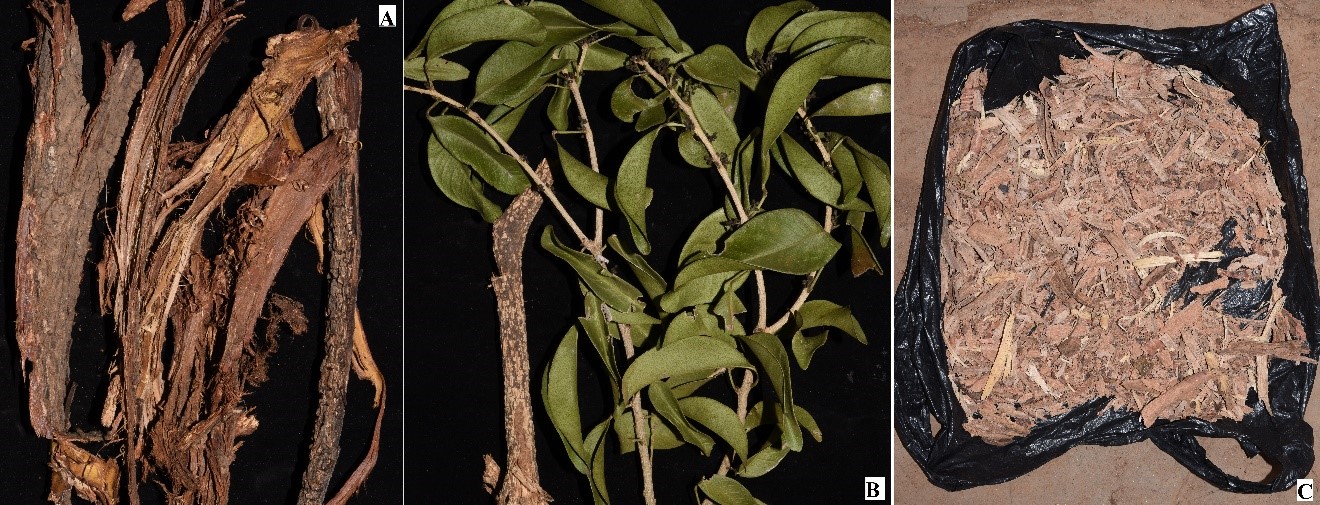

Medicinal plants sold at Mutomo market. A. Bark of Terminalia brownii, B. Leaves of Vepris simplicifolia, C. Bark of Cassia abbreviata (Image by SAJOREC and NMK)