Name:HU Guangwan
Tell:
Email:guangwanhu@wbgcas.cn
Organization:Wuhan Botanical Garden
A New Species of Croton from a Madagascan Lineage Discovered in Kenya
2020-06-04
With about 1300 species in the world, Croton is the second biggest genus in Euphorbiaceae which is only smaller than Euphorbia. There are only 23 species in China. Croton has big diversity in life forms including trees, shrubs, herbs, and a few lianas and its classification is rather difficult. Croton is widely distributed in tropical regions and most abundant in the neotropics. Although toxic, many species of this genus are used as medicine. One famous example is “Ba Dou”, the dry fruit of Croton tiglium, which is a well-known laxative in Chinese Traditional Medicine.
During field investigations at the coast of Kenya, a plant of Euphorbiaceae was collected from the Sacred Kaya Kinondo Forest by Veronicah Mutele Ngumbau, a Kenyan doctoral candidate from the Research Group on Flora and Plant Taxonomy in Eastern Africa in Wuhan Botanical Garden.
Initially, she identified it as a member of Mallotus because it was a shrub with opposite leaves and dentate leaf margins. Preliminary DNA sequencing and a review of the literature of Madagascan Croton revealed that the species belonged to Croton and was morphologically similar to some Croton species endemic to Madagascar and nearby islands. Strangely, though, it differed greatly from all known species of Croton in East Africa.
According to the phylogeny tree based on sequence data of the nuclear ITS region and chloroplast trnL-F region, this species was embedded within the group of northern Malagasy species. Morphological and Molecular phylogenetic evidence suggested that the species was closely related to some endemic Croton species to Madagascar.
Under the guidance of Professor WANG Qingfeng and HU Guangwan, a new species of Croton was identified through careful morphological comparison and named Croton kinondonesis G.W.Hu, V.M.Ngumbau & Q.F.Wang.
The new species is morphologically similar to Croton mayottae and C. menabeensis. Compared with the former, the new species can be characterized by its filamentous and caducous stipules, coarsely serrate leaf margins, and abaxial glands in the base of the secondary veins; Compared with the latter, it can be distinguished by the shape of leaf bases (heart-shaped) and the appearing sites of glands. Croton mayottae is endemic to the Mayotte island of the Comoros Archipelago in north Madagascar, and C. menabeensis is found only in northwestern Madagascar. Based on the geographical distribution of the new species and the two relatives and other closely related species, it is possible that Croton has experienced a dispersal from Madagascar to the African continent via the Comoros Islands, and this route is most likely caused by ocean currents.
The results were published on the international journal of plant taxonomy, Systematic Botany, titled " A New Species ofCroton (Euphorbiaceae) from a Madagascan Lineage Discovered in Coastal Kenya".
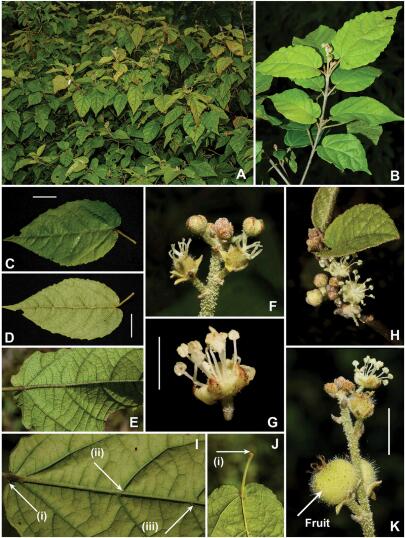
Croton kinondonesis G.W.Hu, V.M.Ngumbau & Q.F.Wang (Image by WBG)
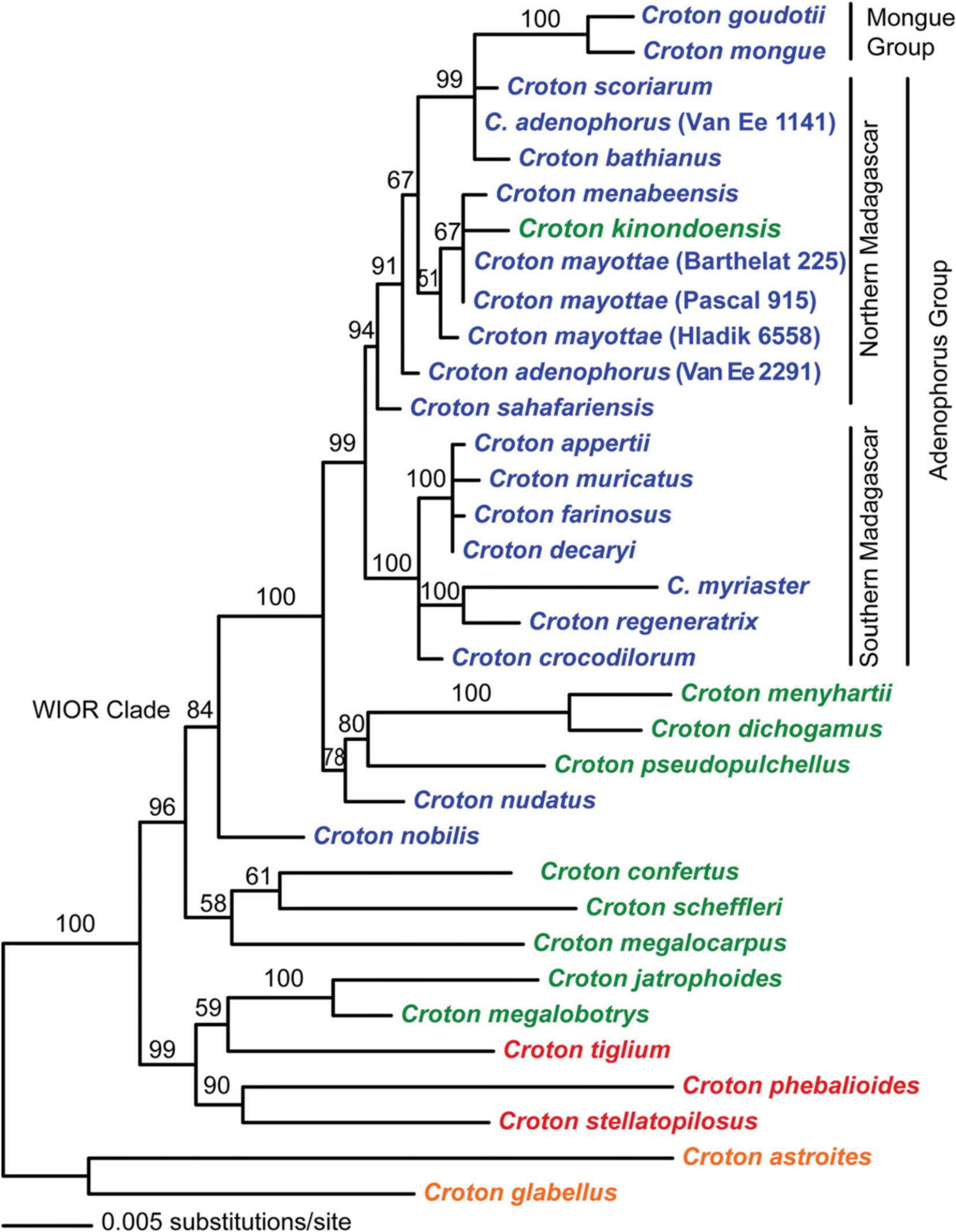
Phylogenetic tree based on ITS and trnL-F data (Taxa in orange are from the New world, in red from Asia and Australia, in green from continental Africa, and in blue from Madagascar and the Comoro Islands) (Image by WBG)