Name:Ming-Quan Guo
Tell:
Email:guomq@wbgcas.cn
Organization:Wuhan Botanical Garden
How to Determine the Anti-anaerobic Activity of Drug Candidate?
2020-07-16
Human infection caused by anaerobic bacteria, such as Bacteroides, Clostridium, Prevotella, Fusobacterium, Bilophila and Sutterella spp., are common and can lead to various human diseases range from local abscesses to life-threatening outcomes.
Traditionally, the treatments of anaerobic infections were safely administered based on empirical broad-spectrum antimicrobial therapy. However, because of the global change of the resistance patterns of anaerobes over the past decades, the direct therapy against anaerobic organisms has been increasingly unpredictable, which often leads to clinical failure. Therefore, huge amount of effort is being implemented for developing new therapies from diversified drug candidates and updating the anti-anaerobic patterns of the clinical isolates, in which the susceptibility testing between the anaerobes and drug or drug candidates is of paramount importance.
Due to the fastidious nature of anaerobic bacteria (low oxygen or oxygen-free atmosphere is required for them to multiply) and the slow growth of the organism, a time- and cost-efficient method for the determination of the anti-anaerobic activity of a drug candidate is not readily available.
According to the characteristics of acid produced by anaerobic bacteria metabolism, the Plant Chemical Biology Research Group at Wuhan Botanical Garden led by Prof. GUO Mingquan proposed to use the metabolic acidity in culture as a universal indicator of the activities of anaerobes to establish a novel method for the determination of the anti-anaerobic activity of drug candidates by automated headspace-gas chromatography (HS-GC-TCD).
Anaerobic bacteria were inoculated in an anaerobic atmosphere or rapidly using sterile syringe in an air-tight manner, and incubated with and without drugs for 48h. The metabolic acidities of the cultured media were used as an indicator of cell activities and measured as end products in place by HS-GC-TCD after being completely converted to CO2 with sodium bicarbonate.
The present method is precise, accurate and suitable for the determination of anti-anaerobic activities of drug candidates for drug screening purpose. Compared to the conventional method, the present method is safer with regard to cross contamination and more flexible in drug species.
This work was jointly supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China and Major Project for Special Technology Innovation of Hubei Province-Sino-foreign Cooperation Project.
Relevant research results have been published in Journal of Chromatography A entitled “A phase conversion headspace analysis technique for the determination of anti-anaerobic activity of drug candidate based on the metabolic acidity change in culture medium”.
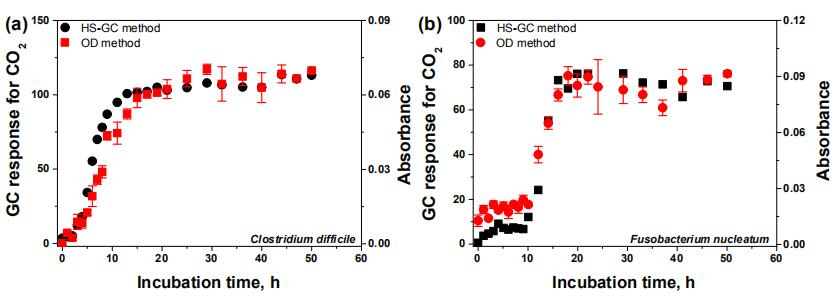
The growth curves of (a) one representative gram-positive anaerobe (C. difficile) and (b) one representative gram-negative anaerobe (F. nucleatum) obtained by both HS-GC method and optical density method (Image by WBG)