Name:Mingquan Guo
Tell:
Email:guomq@wbgcas.cn
Organization:Wuhan Botanical Garden
C. spinarum Possesses Phenolic Compounds with Remarkable Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Hepatoprotective Activities
2021-07-16
Carissa spinarum is a well-known medicinal plant in some African countries, known as ‘magic shrub’ for its wide range of indications. Some studies have been conducted mostly on its chemical constituents and ethnopharmacological uses. However, the active compounds responsible for its potential antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective activities from the root barks of C. spinarum have not been explored yet.
Researcher from Wuhan Botanical Garden conducted the preliminary antioxidant and COX-2 inhibition screening for four partition extracts with different polarity from C. spinarum, using 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) methods, and COX-2 inhibitor screening assay, respectively.
Results revealed that ethyl acetate (EA) fraction exhibited most promising activities in all three preliminary assays above. In order to search for potential antioxidants and COX-2 inhibitors from the active fraction, the EA part was selected for further phytochemical isolation using modern phytochemical techniques and comprehensive spectroscopic methods.
10 compounds (1-10), including a new one (compound 5), were isolated and subsequently tested for their antioxidant and COX-2 inhibition activities. Among them, compound 9 possessed the best radical scavenging capacity with lower IC50 than that of positive control vitamin C with DPPH method, and compounds 2, 6, 7 and 9 showed better total antioxidant capacity than vitamin C in all tested concentrations with FRAP method.
Meanwhile, the COX-2 inhibitor screening results revealed that compounds 1-7 and 9-10 displayed different potentials for COX-2 inhibition, among which compounds 1-6 and 9 exhibited IC50 values lower than 1.0 μM, which were even better than the positive anti-inflammatory drug like indomethacin. In this context, compounds 2 and 9 with potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities in both assays were selected and further evaluated for their hepatoprotective activity using a H2O2- induced L02 cell injury model. As a consequence, these two compounds were revealed to exhibit obvious hepatoprotective activities by improving the L02 cell viability and reducing the reactive oxygen species (ROS) production.
This study provided the first piece of evidence to reveal most potent phenolic compounds from the root barks of C. spinarum responsible for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective activities, and these potential compounds could be further explored as natural remedies for hepatocyte damage related applications in the near future.
This research was supervised by Prof. GUO Mingquan, and Dr. LIU Ye from Wuhan Botanical Garden was the first author. This research was partially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province.
The above results were published in Antioxidants entitled “Phenolic Compounds fromCarissa spinarum Are Characterized by Their Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Hepatoprotective Activities”.
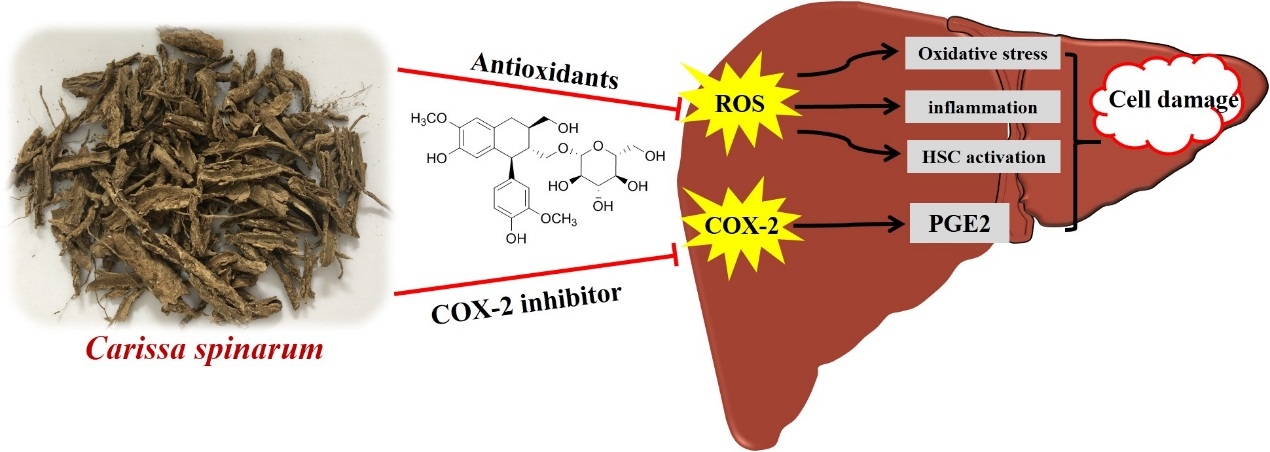
Phenolic compounds from Carissa spinarum are characterized by their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective activities (Image by LIU Ye)