Name:LIU Guihua
Tell:
Email:liugh@wbgcas.cn
Organization:Wuhan Botanical Garden
Inter-annual Variation Affects Microbial Communities More Than Detritus Imput Manipulation
2021-10-26
Microbes regulate soil carbon and nutrients cycles in terrestrial ecosystems through impacting the decomposition and incorporation of organic matter in soils. While, soil microbial communities are profoundly affected by changes in biotic and abiotic factors as a consequence of global change. How the soil microbial community responds to the inter - annual variations remains unclear.
Supervised by Prof. LIU Guihua and CHENG Xiaoli, WU Junjun, a research assistant of Wuhan Botanical Garden, conducted a detritus input and removal treatment in a coniferous forest ecosystem in subtropical China, to measure the annual soil microbial community structure and environmental variables from 2015 to 2017 and evaluate the inter-annual variation in soil microbial community under shift in plant detritus input scenario.
This study demonstrated that soil microbial community structure and abundance significantly differed among years and detritus input treatments. The effects of the inter-annual variations in soil microbial community were significantly more visible than that of shifts in plant detritus input, owing to the temporal alterations in microclimates and substrate availability.
Litter removal or root exclusion could reduce microbial biomass in various ecosystems. In contrast, litter addition had less effect on microbial biomass, and the significant effect appeared only after three years of detritus input manipulation. Litter removal, especially the no input treatment significantly increased the fungi to bacteria and Gram-positive to Gram-negative bacteria ratios after the first and the second year of detritus input manipulations. However, litter addition did not significantly affect these parameters.
A clear discrimination of microbial community structure between the different detritus input manipulation treatment in the time after half and one year of detritus input manipulation, which became distinct in the time after two and three years. Both fungi to bacteria and Gram-positive to Gram-negative bacteria ratios were negatively related to the carbon to nitrogen ratio, recalcitrance index of carbon and nitrogen. Soil basal respiration was negatively associated with fungi to bacteria ratio across all detritus input treatments.
Results indicated that the integrated analysis of inter-annual patterns of microbial community structure and environmental variables could help to elucidate the response of soil microbial community to global change. Furthermore, the predictable response of microbial community to plant detritus input change could also provide important insight for comprehending the consequences of shifts in above- and belowground productivity on ecosystem function of global forest ecosystems.
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the "Strategic Priority Research Program B of the Chinese Academy of Sciences”. Results have been published in Ecological Indicators entitled “Case study on a coniferous plantation site about inter-annual shifts in microbial communities under short-term detritus input manipulations”.
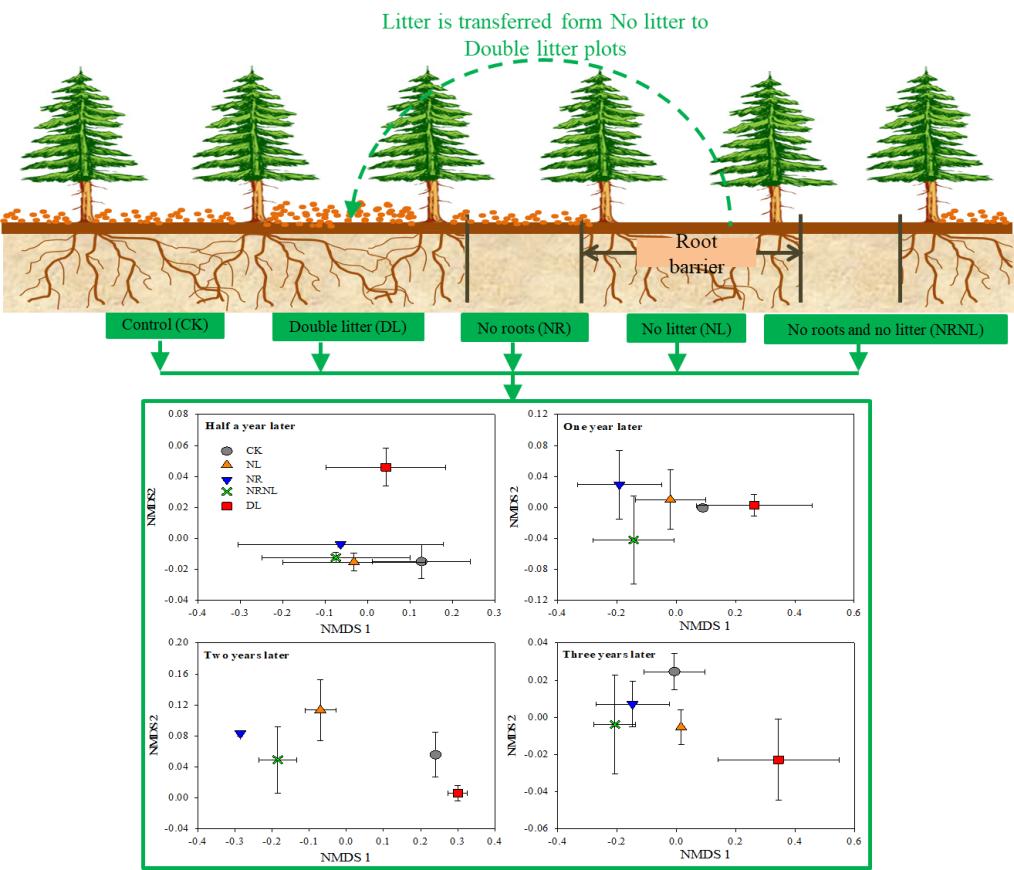
The variation in microbial community structure among different plant detritus input manipulations over study period (Image by WU Junjun)