Hoya is the second largest genus in Apocynaceae-Asclepiadoideae with at least 300 species. It has been grown in botanical gardens around the world due to the showy flowers, ease of growing and popularity as ornamental plants. However, phylogenetic relationships among most Hoya species are not yet fully resolved.
Researchers from Wuhan Botanical Garden compared and characterized the chloroplast genomes among 31 selected species of Hoya group, identified and selected molecular markers suitable for population genetics, reconstructed the species relationships of the six extant clades of the Hoya group.
Results revealed that all plastomes (figure 1) shared a unique chloroplast quasi-tripartite genome structure for Hoya and Dischidia with a strongly reduced small single copy (SSC) and extremely enlarged inverted repeats (IR). Their lengths varied from 175,404 bp in Hoya lacunosa to 179,069 bp in H. ariadna, mainly because of length variation in large single copy (LSC) (80,795 bp in H.liangii to 92,072 bp in Hoya_sp2_ZCF6006).
Highly divergent regions (ndhF, ycf1, rpl22, matK, trnT-trnL, and trnL-trnF) and repeats (-mono, -tri, -Penta, and -hexanucleotides) that could potentially serve as molecular markers for phylogenetics were identified. The phylogenetic analyses supported Clemensiella as a distinct genus (figure 3). Hoya ignorata is resolved as a relative to Clade VI species.
This study provides insights into the evolutionary relationships and biogeographic history of the Hoya group species.
This study was funded by the Biological Resources Program, Chinese Academy of Sciences(CAS), China National Plant Specimen Resource Center, International Partnership Program, CAS, and Sino-Africa Joint Research Center, CAS. Wyclif Ochieng Odago, a Kenyan student is the first author. Professor HU Guangwan and ZHANG Caifei are the corresponding authors. Several students from the group took part in the study as well.
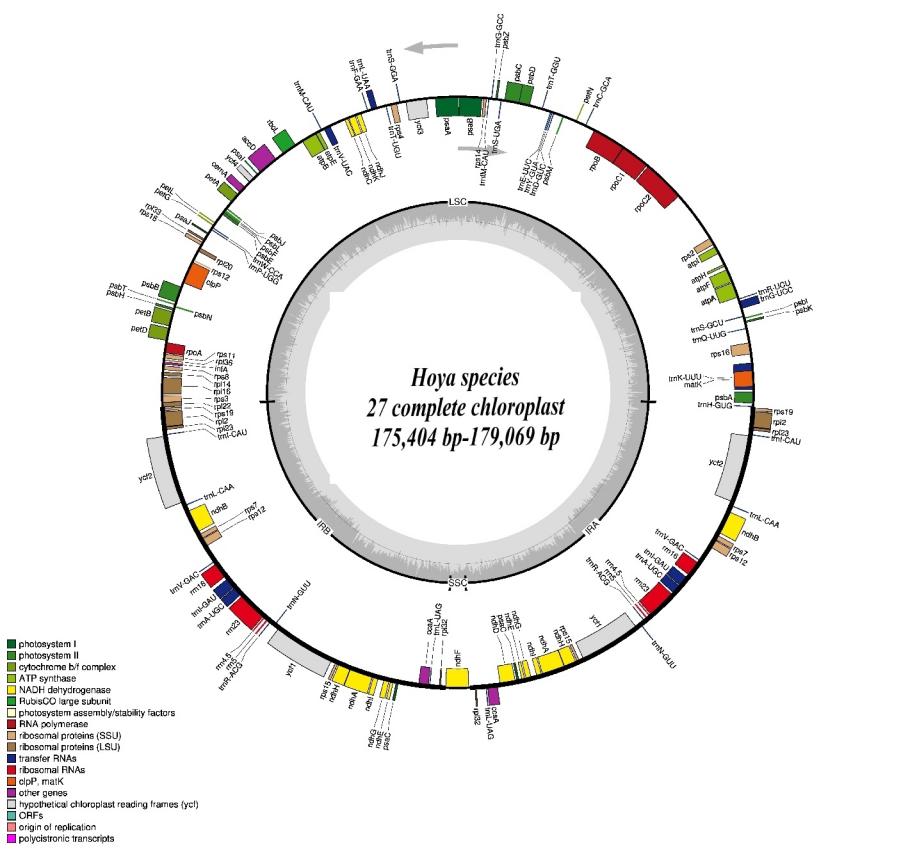
Figure 1. The genome maps of 27 Hoya species (Image by WBG)

Figure 2. Rearrangements in 7 Hoya plastomes using the mauve multiple alignment algorithm (Image by WBG)

Figure 3. Phylogenetic tree of Hoya inferred from 57 species using ML. CDS tree reconstruction is rooted with Marsdenia and Jasminanthes as outgroups (Image by WBG)


