Name:HU Guangwan
Tell:
Email:guangwanhu@wbgcas.cn
Organization:Wuhan Botanical Garden
How Will Climate Change Impact Aloe Species in East Africa?
2022-11-03
Climate change poses major threats to plant species’ survival, particularly those with restricted distribution. Understanding how climate change affects endemic species is critical for conservation efforts. Aloe L. is the leading genus in the Asphodelaceae family with 548 accepted species. About 63 Aloe species occur in Kenya, of which around 50 % are endemic and 48 species of Aloe are recognized in Tanzania. The IUCN Red List lists less than 16 Aloe species as "critically endangered", "endangered", or "vulnerable" from the most threatened categories. However, no conservation management plans have been developed.
The Flora and Plant Taxonomy in Eastern Africa Research Group of Wuhan Botanical Garden analyzed the impacts of climate change on the potential distribution of three endemic Aloe species ( Aloe ballyi Reynolds, Aloe classenii Reynolds, and Aloe penduliflora Baker ) critically endangered in East Africa in the future (the years 2050 and 2070) using niche modeling.
Two representative concentration pathways scenarios (RCP4.5 and RCP8.5) are used to project the contraction of suitable habitats for the species. The environmental and bioclimatic variables (potential evapotranspiration, soil sedimentary rocks, temperature and precipitation) had a great impact on the distribution of the three Aloe species. Potential suitable habitats for A.ballyi and A. penduliflora are limited to the coastal region of Kenya and some regions in Tanzania, whereas habitat for A. classenii is limited to a small region in the coastal region of kenya. Despite the expected expansion of A. penduliflora habitat, the existing distribution of suitable habitat for all three species is expected to shrink. The original habitats of A. ballyi and A. classenii are projected to shrink by 44% and 34% in the two representative concentration pathways scenarios (RCP4.5 and RCP8.5).
These models indicate that climate change may lead to the loss of a large area of current Aloe habitat, highlighting the need of attention to the conservation of Aloe in Kenya.
The research entitled “Modeling Impacts of Climate Change on the Potential Distribution of Three EndemicAloeSpecies Critically Endangered in East Africa” was published in the journal of Ecological Informatics. The National Natural Science Foundation of China and Sino-Africa Joint Research Center, CAS supported this work.
Elijah Mbandi Mkala together with one Kenyan students Elizabeth Syowai Mutinda are the first authors. Professor HU Guangwan is the corresponding author. Several students from the group participated in the study.
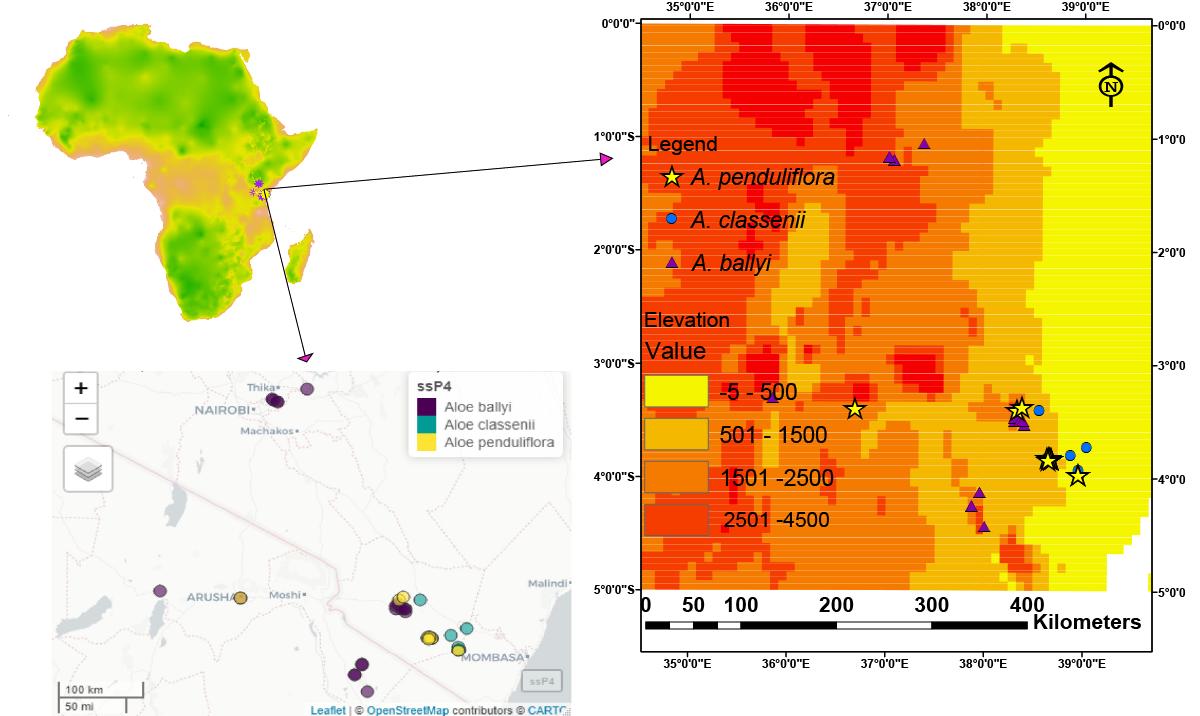
Map showing the known distribution range of A. ballyi (purple), A. classenii (light blue) and A. penduliflora (yellow) distributed in Kenya including some regions in Tanzania (Image by WBG)
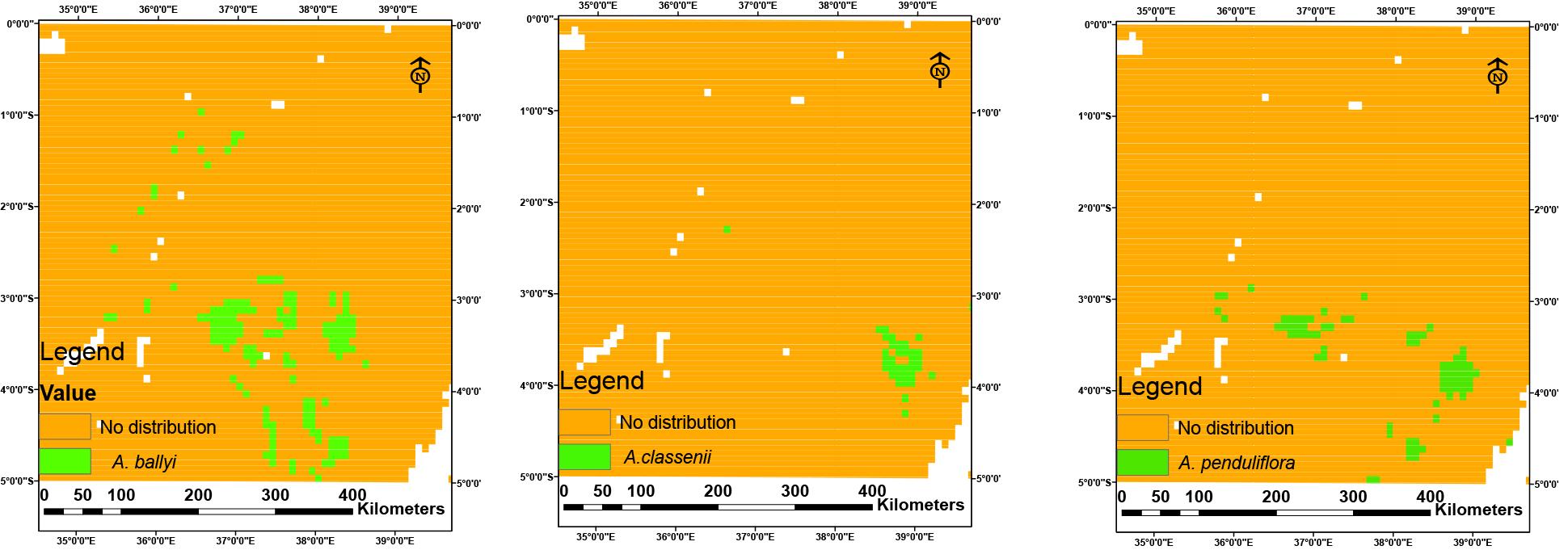
Current maps showing the distribution range of A. ballyi, A. classenii and A. penduliflora (green) and where the species were not distributed indicated in yellow color (Image by WBG)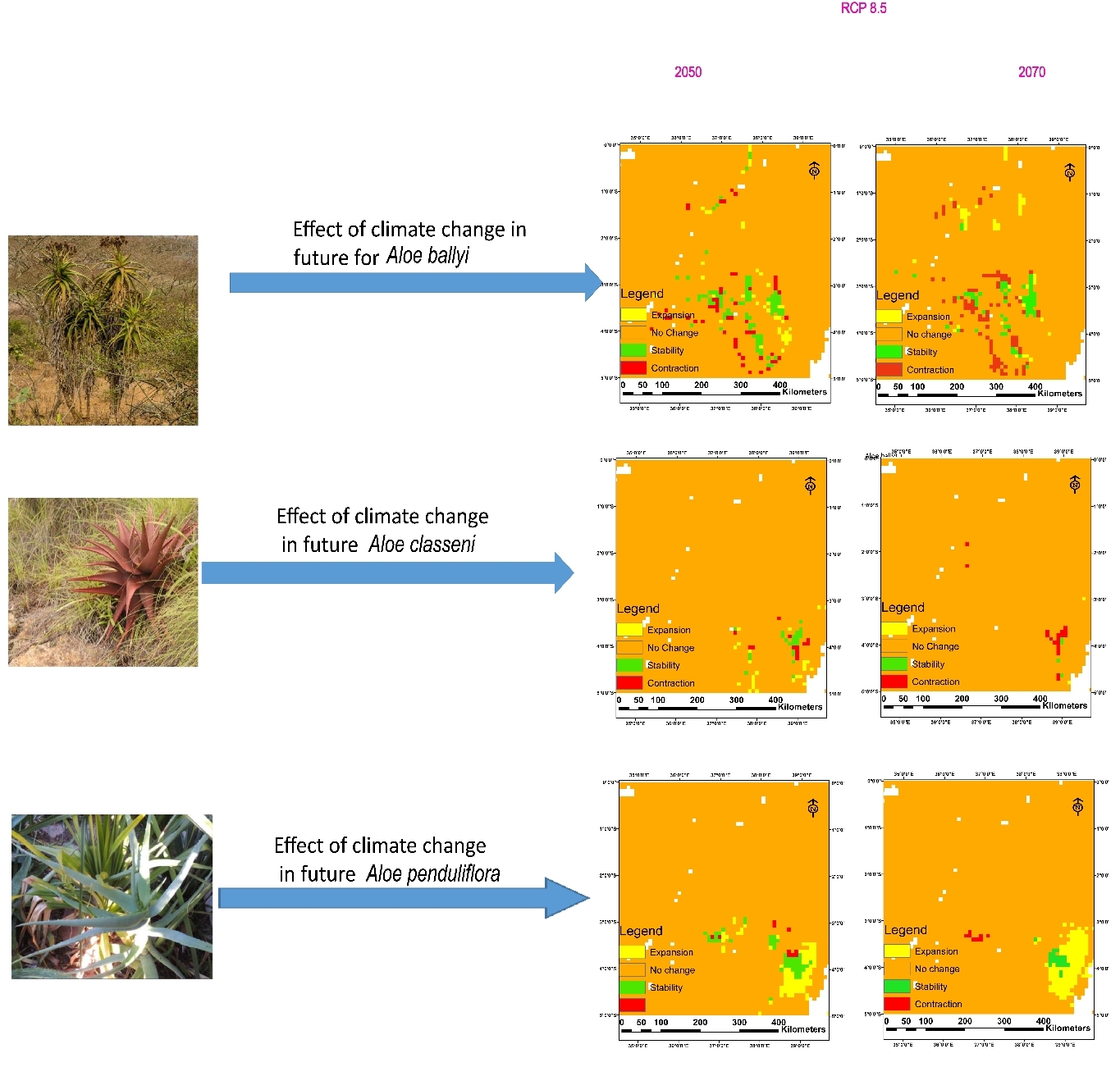
Future climatic scenarios and estimated putative distribution ranges for A. ballyi, A. clasenii, and A. penduliflora in RCP 8.5 for the years 2050 and 2070 are depicted on maps (Image by WBG)
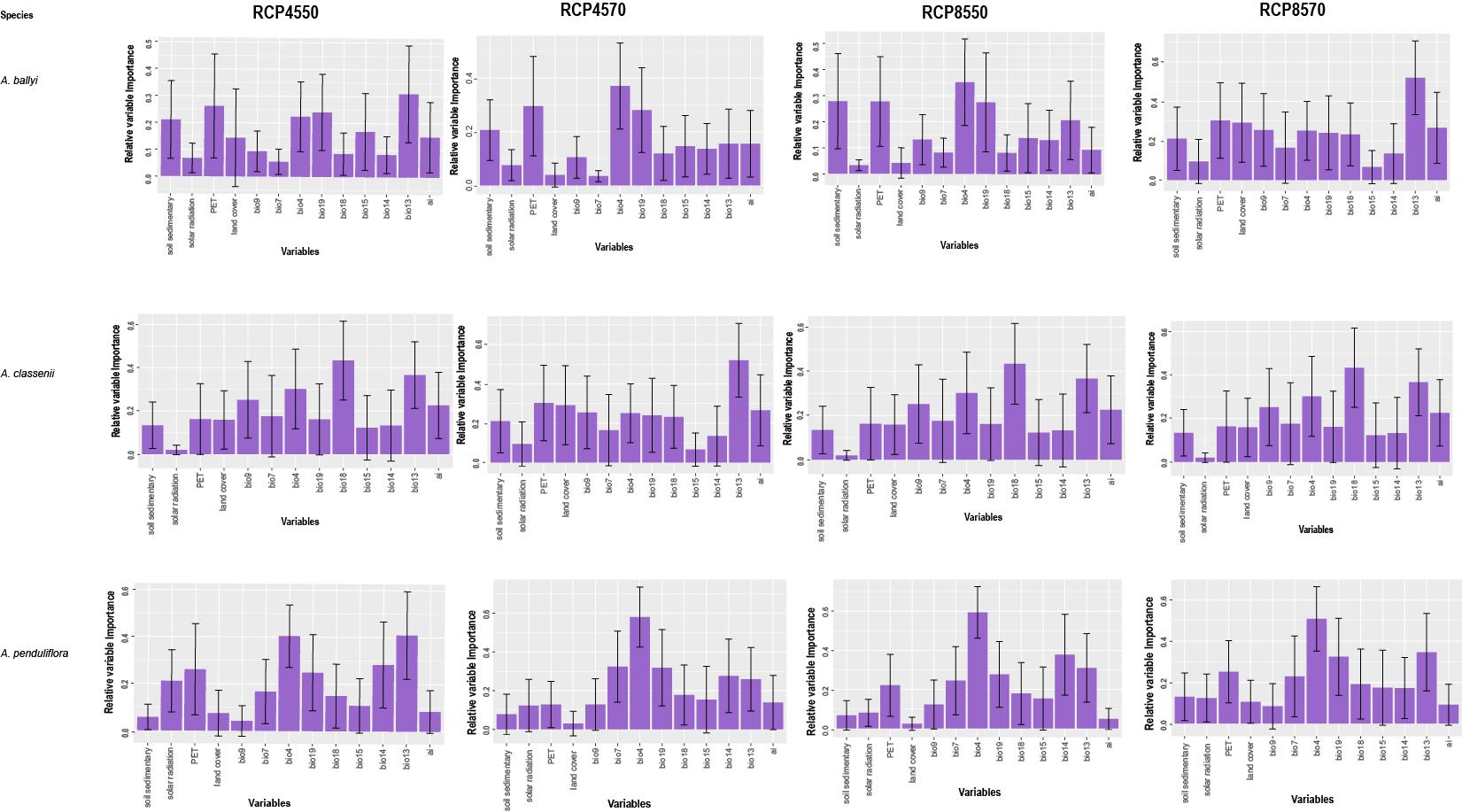
Estimated variable importance for the studied environmental variables based on the Pearson correlation and the area under the curve (AUC) metric for A. ballyi, A. classenii and A. penduliflora (Image by WBG)