Name:DANG Haishan
Tell:
Email:dangkey@wbgcas.cn
Organization:Wuhan Botanical Garden
Research Unveils Patterns of Species Diversity and the Determinants in Temperate Forest
2022-11-15
The Qinling Mountains, which run east- west and serve as the geographical boundary between the northern and southern China as well as the climatic demarcation line between the subtropical and warm temperate zones in China, are of ecological significance in biodiversity research.
To determine the underlying causes of the variations of species diversity in the temperate forest, Dr. HE Rui, supervised by Prof. DANG Haishan from Wuhan Botanical Garden, applied multivariate linear regression analysis to test the effects of biotic and abiotic factors on alpha- diversity, LCBD (Local Contribution to Beta Diversity) and SCBD (Species Contribution to Beta Diversity), and used variation partitioning in combination with environmental variables and spatial distance to determine the contribution of environment- related variations versus spatial variations in a fully mapped 25- ha permanent forest plot in the Qinling Mountains of north- central China.
With regard to alpha- diversity, results showed that the species abundance and richness had positive correlation with soil available phosphorus, and had significant negative correlation with slope.
For the beta- diversity, both environmental and spatial variables had significant influence on the variations of beta- diversity, explaining 46% of the variation in community composition of the permanent forest plot. Nearly 60% of the variation of LCBD in the understory layer was explained jointly by biological factors, soil features and topographic variables. However, in the substory layer and canopy layer, these variables explained only 40% and 29% variations of LCBD.
High species abundance was found to be associated with high SCBD values regardless of forest vertical strata, and niche position, as one of the ecological traits, significantly affected the variations of SCBD in the substory and canopy layers.
Under the exploration of the potential influencing factors of species diversity from the perspective of vertical stratification of forest community, the study enlightens the biotic factors and how species diversity in forest responds to environmental conditions and how it is influenced by biotic factors and ecological traits of species. The study also provides novelty for the protection of forest biodiversity and the revelation of the mechanism of species coexistence.
The research was published in Forest Ecosystems entitled as “Patterns of species diversity and its determinants in a temperate deciduous broad-leaved forest”. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the Meituan Qingshan Special Commonweal Fund of China Environmental Protection Foundation.
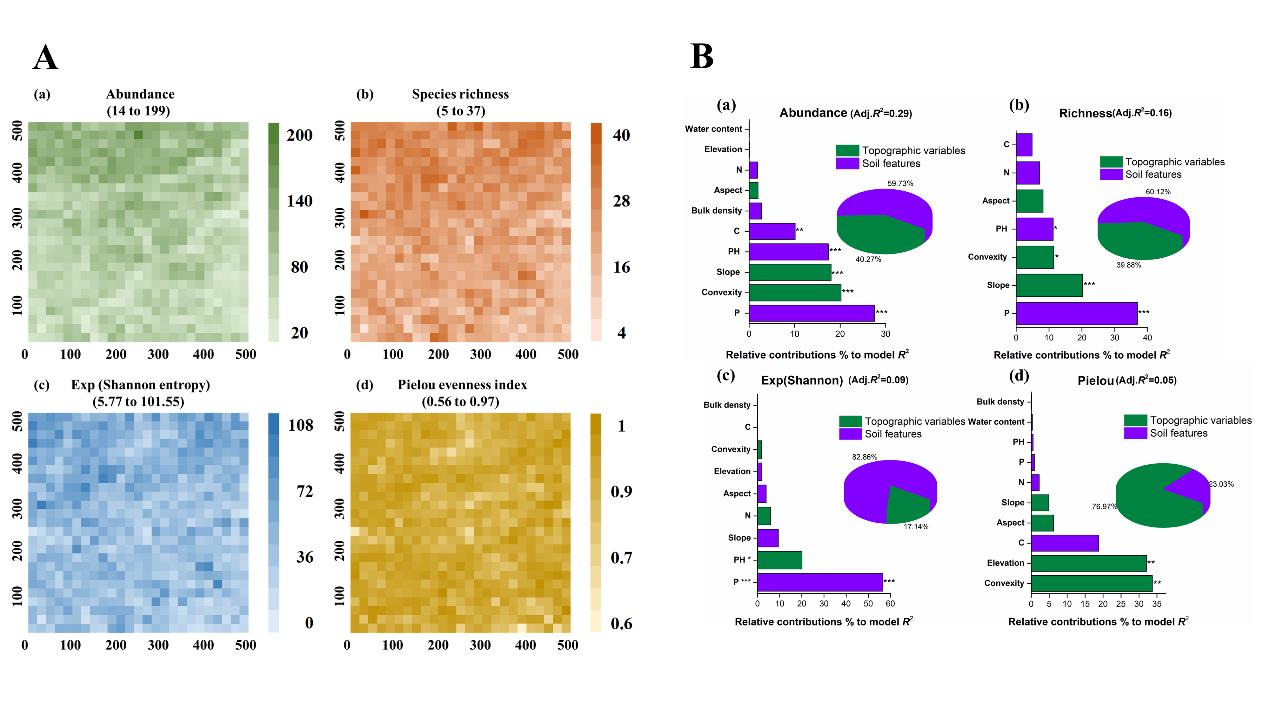
The distribution of the alpha-diversity among the 625 subplots (20 m × 20 m) within the 25-ha forest plot and the effects of the environmental factors on the alpha- diversity (Image by WBG)
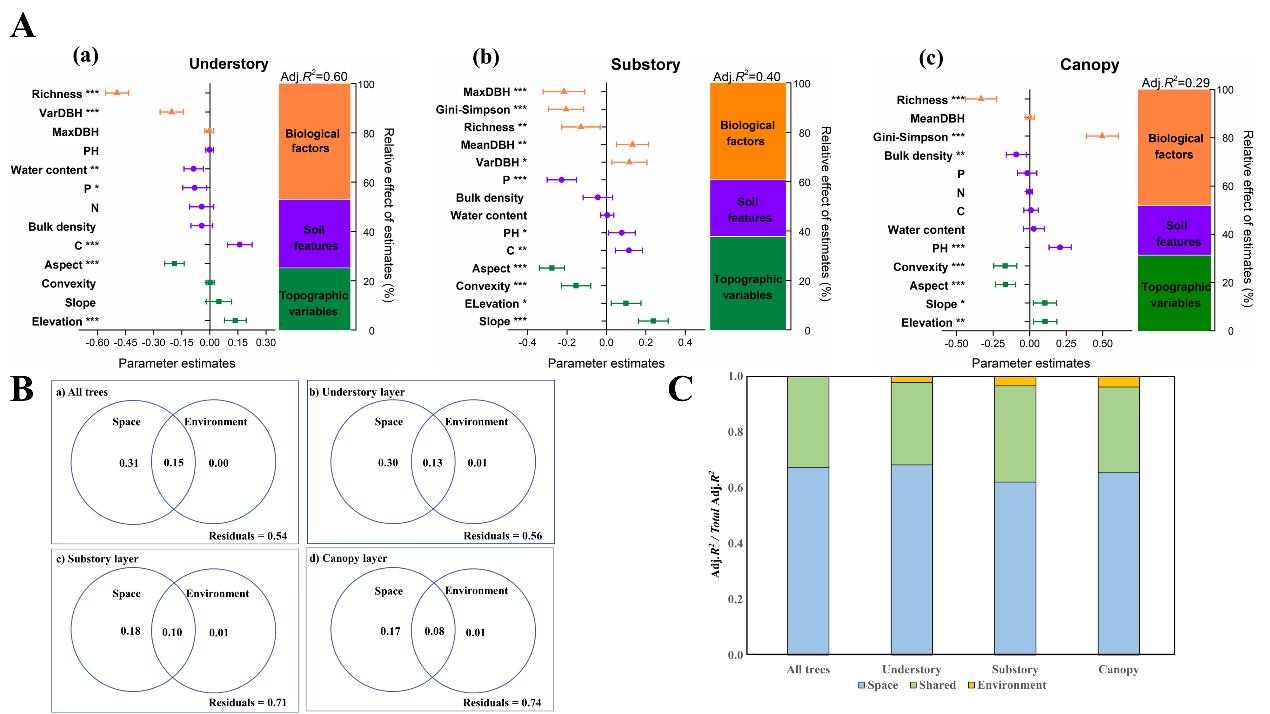
The relative importance of biological factors, soil features, and topographic variables to LCBD (expressed as the percentage of explained variance) and the variation partitioning of community composition using environmental and spatial data (Image by WBG)