Name:CHEN Guilin HU Guangwan
Tell:
Email:glchen@wbgcas.cn guangwanhu@wbgcas.cn
Organization:Wuhan Botanical Garden
Study Reveals the Potential Antioxidative and Anti-Hyperuricemic Components in Chinese Medicine Rodgersia podophylla A. Gray
2024-01-03
Rodgersia podophylla A. Gray (R. podophylla) is a traditional Chinese medicine, which exhibits antioxidant, antibacterial, immune-enhancing, hepatoprotective, antimalarial, anticancer, and anti-inflammatory properties. However, the specific components responsible for these effects have not been revealed.
Researchers from Wuhan Botanical Garden used bio-affinity ultrafiltration liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (UF-LC-MS), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and xanthine oxidase (XOD) as the target enzymes to study the components of R. podophylla extracts with antioxidant and anti-hyperuricemic activities.
The results displayed that norbergenin, catechin, procyanidin B2, 4-O-galloylbergenin, 11-O-galloylbergenin, and gallic acid were suggested as potential compounds with antioxidant activity, while gallic acid, 11-O-galloylbergenin, catechin, bergenin, and procyanidin B2 were recognized as potential ligands with anti-hyperuricemic activity in R. podophylla, respectively. Molecular docking analysis showed that these compounds had strong interactions with the target enzymes. In addition, bergenin was further confirmed to be a potential XOD inhibitor in vitro.
In summary, this study represented the first application of the UF-LC-MS method for the rapid screening of bioactive compounds in R. podophylla extracts, specifically targeting its antioxidant and anti-hyperuricemia properties.
This research not only provided novel evidence to support the antioxidant and anti-hyperuricemic properties of R. podophylla, but also clarified the potential bioactive ligands for its further research and application.
Results have been published in the Frontiers in Pharmacology entitled “Potential antioxidative and anti-hyperuricemic components inRodgersia podophyllaA. Gray revealed by bio-affinity ultrafiltration with SOD and XOD”. This research was funded by the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of Chinese Academy of Sciences.

HPLC chromatograms of the chemical constituents in the EA fraction of R. podophylla were obtained after ultrafiltration at 310 nm (Image by WBG)
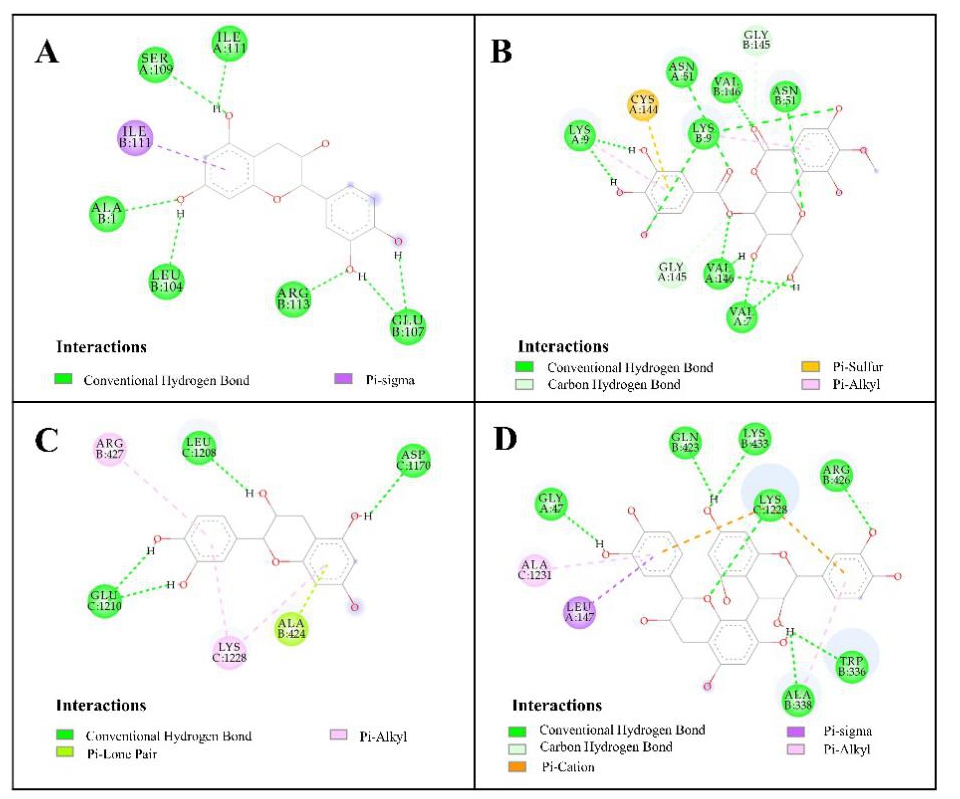
Docked complexes of SOD and XOD: (A), SOD-catechin; (B), SOD-4-O-galloylbergenin; (C), XOD-catechin; (D), XOD-procyanidin B2 (Image by WBG)