Name:HAN Yuepeng
Tell:
Email:yphan@wbgcas.cn
Organization:Wuhan Botanical Garden
Research Unveils the Superior Antioxidant Capacity of Red-fleshed Peach
2024-09-18
Phenolic compounds, a diverse group of secondary metabolites, are widely distributed throughout plant kingdom with immense structures and functions. Besides the well-known physiological functions, phenolic compounds contribute to the overall fruit quality in terms of coloration, flavor, and nutritional value, besides, they also draw considerable attention due to the potential bioactivity.
Peach draws particular attention due to its nutritional properties, with red-fleshed peach standing out for the excellent antioxidant activity. Understanding the metabolic basis will provide a theoretical foundation for the genetic improvement and developing varieties that are rich in bioactive components in peach breeding programs.
Researchers from Wuhan Botanical Garden qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed the concentration and composition of phenolic compounds, and identified differences in phenolic compounds between red-fleshed and non-red-fleshed peaches.
There were significant differences in phenolic compounds and antioxidant activities among red-fleshed and non-red-fleshed peaches, with red ones having higher levels. It was observed that multiple phenolic compounds might act as a determinant role in the overall antioxidant activity. Dynamic changes in antioxidant activities and phenolic compounds content were observed throughout fruit development, with significantly higher phenolic compounds content in the peel than in the flesh. The accumulation of multiple phenolic acids and flavonoids was coordinately enhanced by the increase of anthocyanins in red-fleshed peaches, contributing to their superior antioxidant activity.
The accumulation of multiple compounds of phenolic acids and flavonoids was enhanced coordinately by the increase of synthesis of anthocyanins in red-fleshed peaches, which enhanced the superior antioxidant activity of red-fleshed peaches.
Results have been published in the Food chemistry-X entitled “Metabolic basis for superior antioxidant capacity of red-fleshed peaches”. This project is financially supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Hubei Hongshan Laboratory, the China Agriculture Research System and Sino-Africa Joint Research Center.
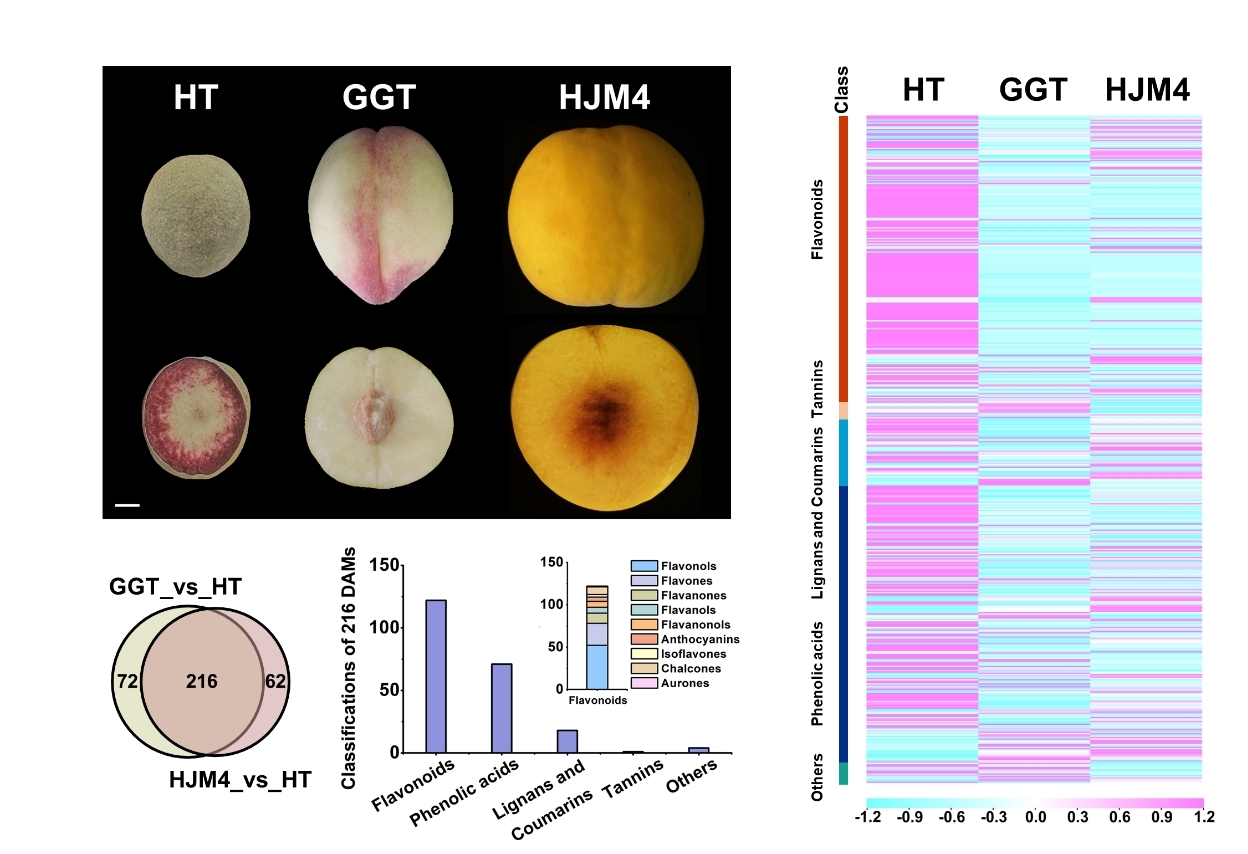
Overview analysis of phenolic metabolites in peach with diverse coloration (Image by WBG)